[객체지향개발론] 08 Grasp Patterns(1) | 09 Grasp Patterns(2) and Advanced concepts
Responsibilities
"Doing" responsibilities
- doing something / initiating action / controlling & coordinating activities
"Knowing" responsibilities
- knowing about data / related objects / things it can derive or calculate
OOD (object oriented design) 에서 responsibilties 가 할당된다.
responsibilities 는 단독으로 act하거나 다른 방법 및 객체와 협력하는 방법을 사용하여 구현된다.
SRP (single responsibility principle)
- 객체는 하나의 Responsibilites 를 가지며, 이를 위해 하나 이상의 operation 을 가진다.
Solid pattern(principle)
- SRP(single responsibility principle)
- OCP(open-closed principle)
- LSP(liskov substitution principle)
- ISP(interface segregation principle)
- DIP(dependency inversion principle)
Responsibility assignment & Interaction Diagrams
- interaction diagram : 객체에 responsibilities 를 할당할 때의 design decision 을 보여줌.
- design decision : 객체에 어떤 메시지를 보낼지 반영함.
🍇GRASP Patterns
- GRASP (General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns)
1️⃣Information Expert
- 객체지향의 기본 principle
- Problem
: responsibilities 가 할당되는 기본 원칙이 무엇인가?
- Solution
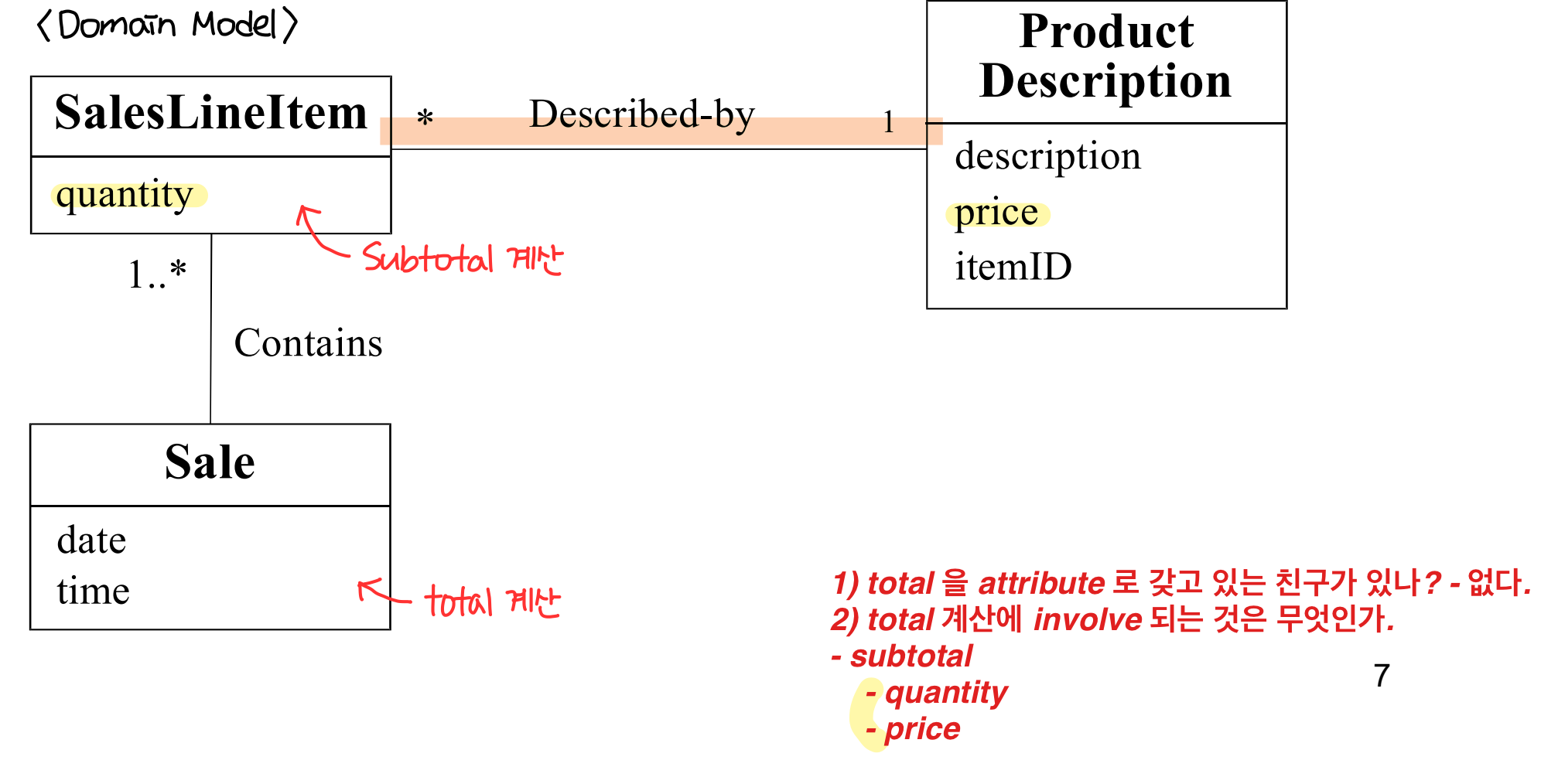
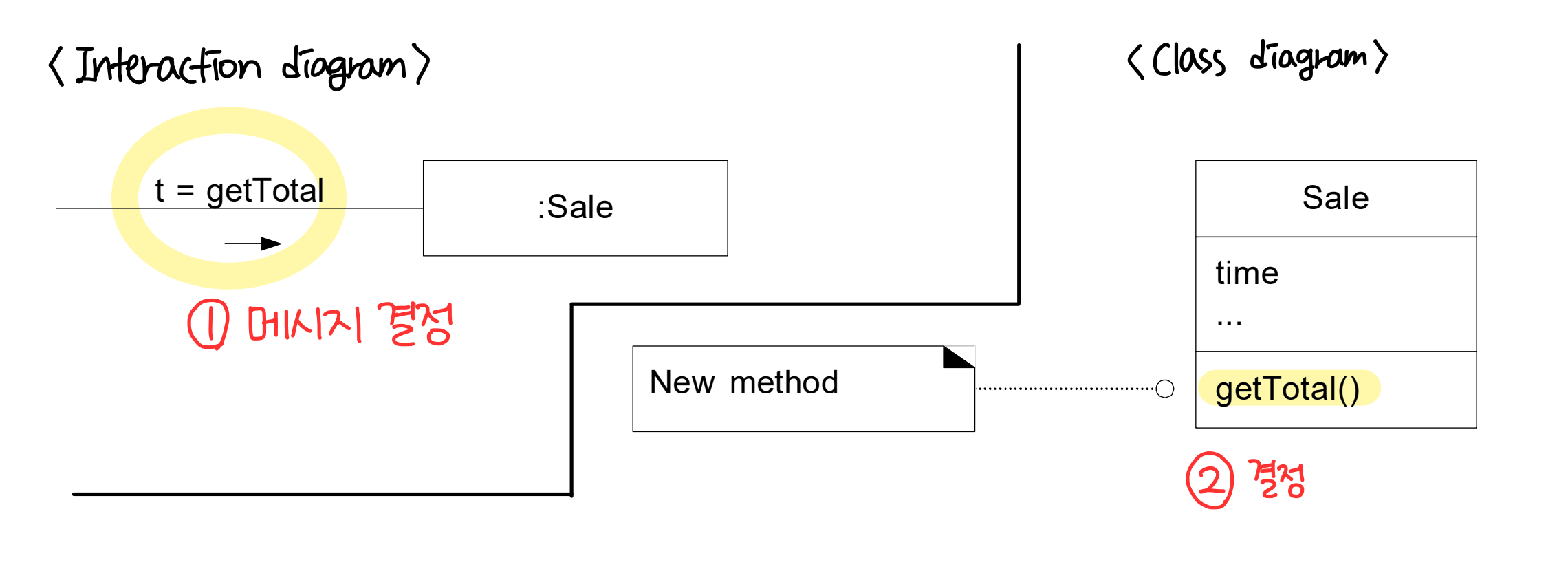
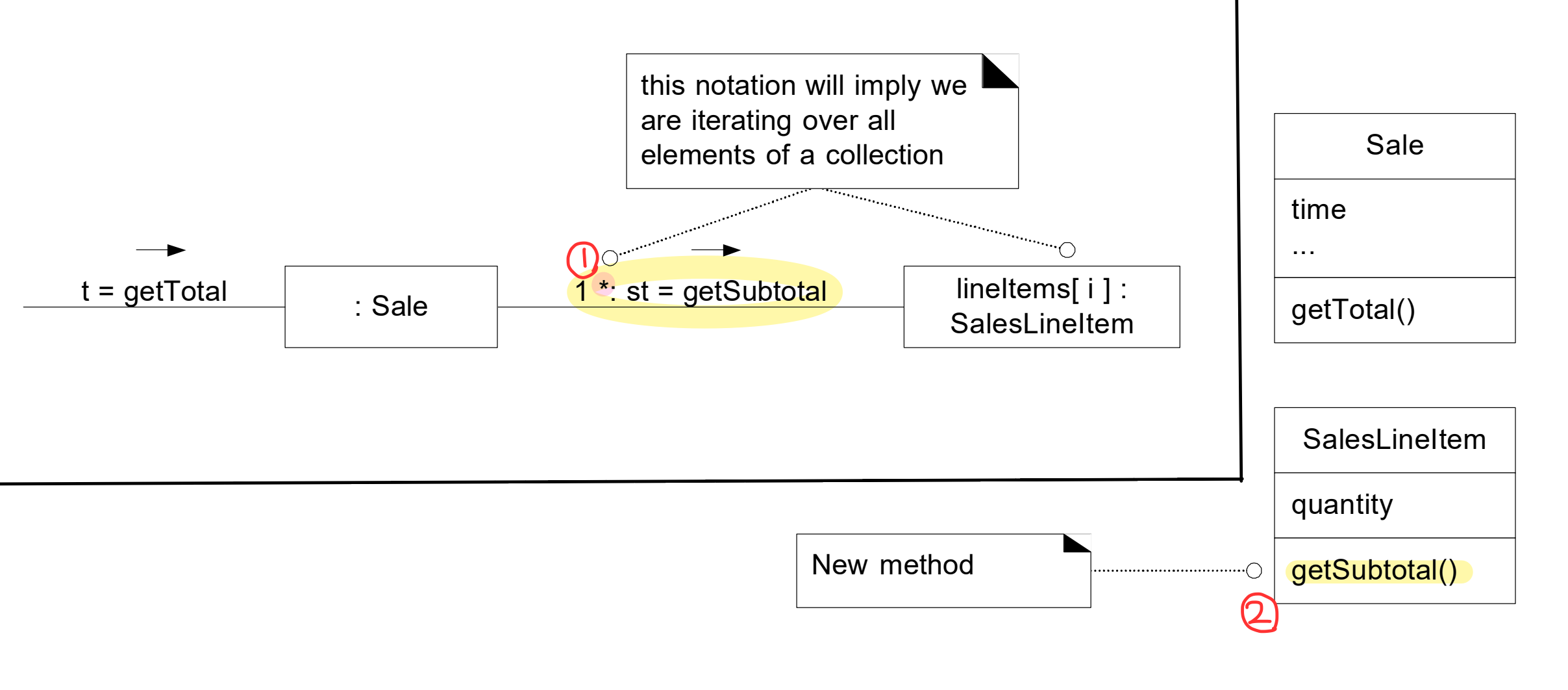
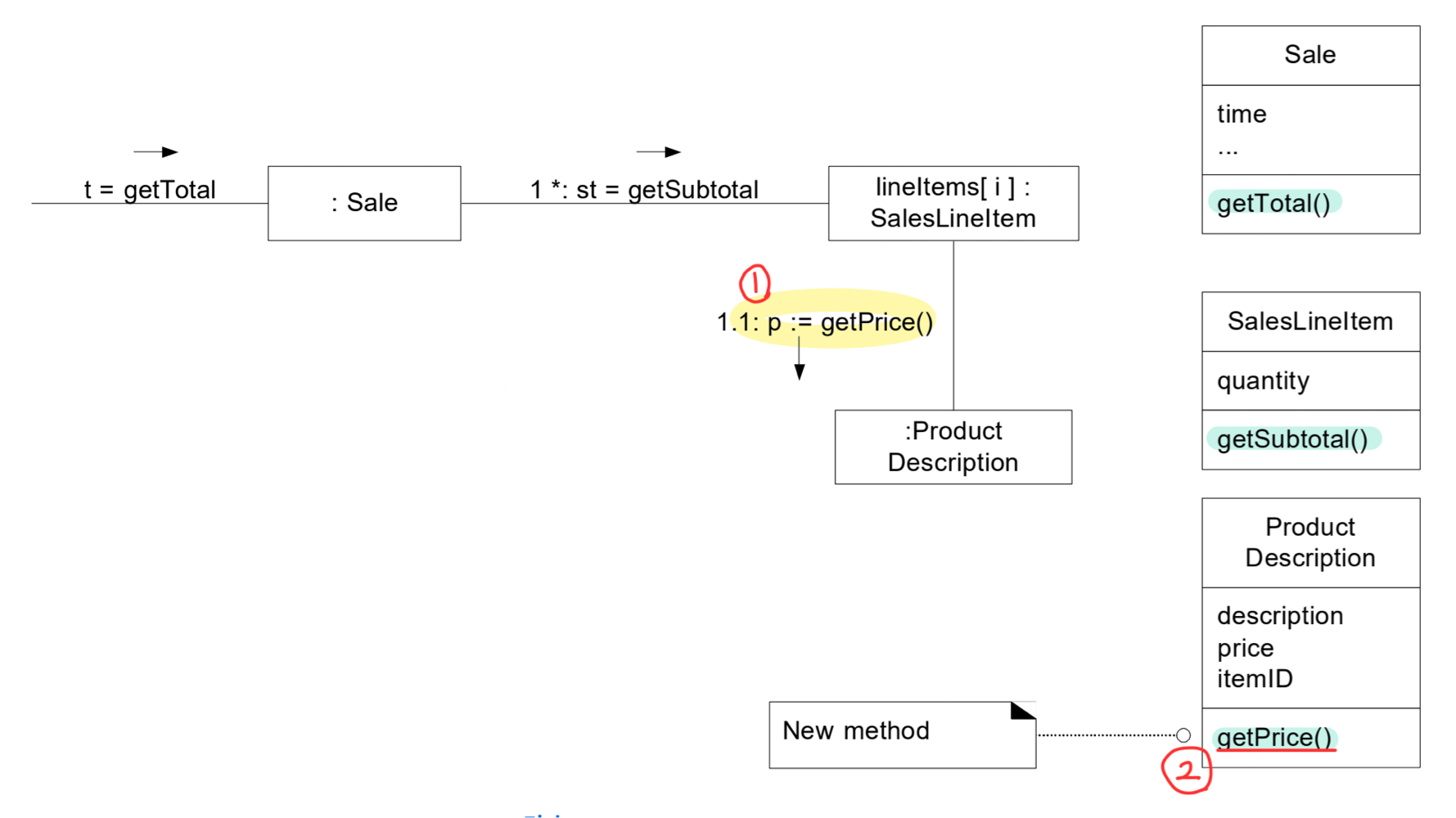
: responsibility 를 수행하는데 필요한 information 을 가진 클래스(information expert) 에게 할당한다. - Example : sale 의 total 을 계산하는 책임을 누구에게 할당할 것인가?
2️⃣Creator
- 객체 생성에 필요
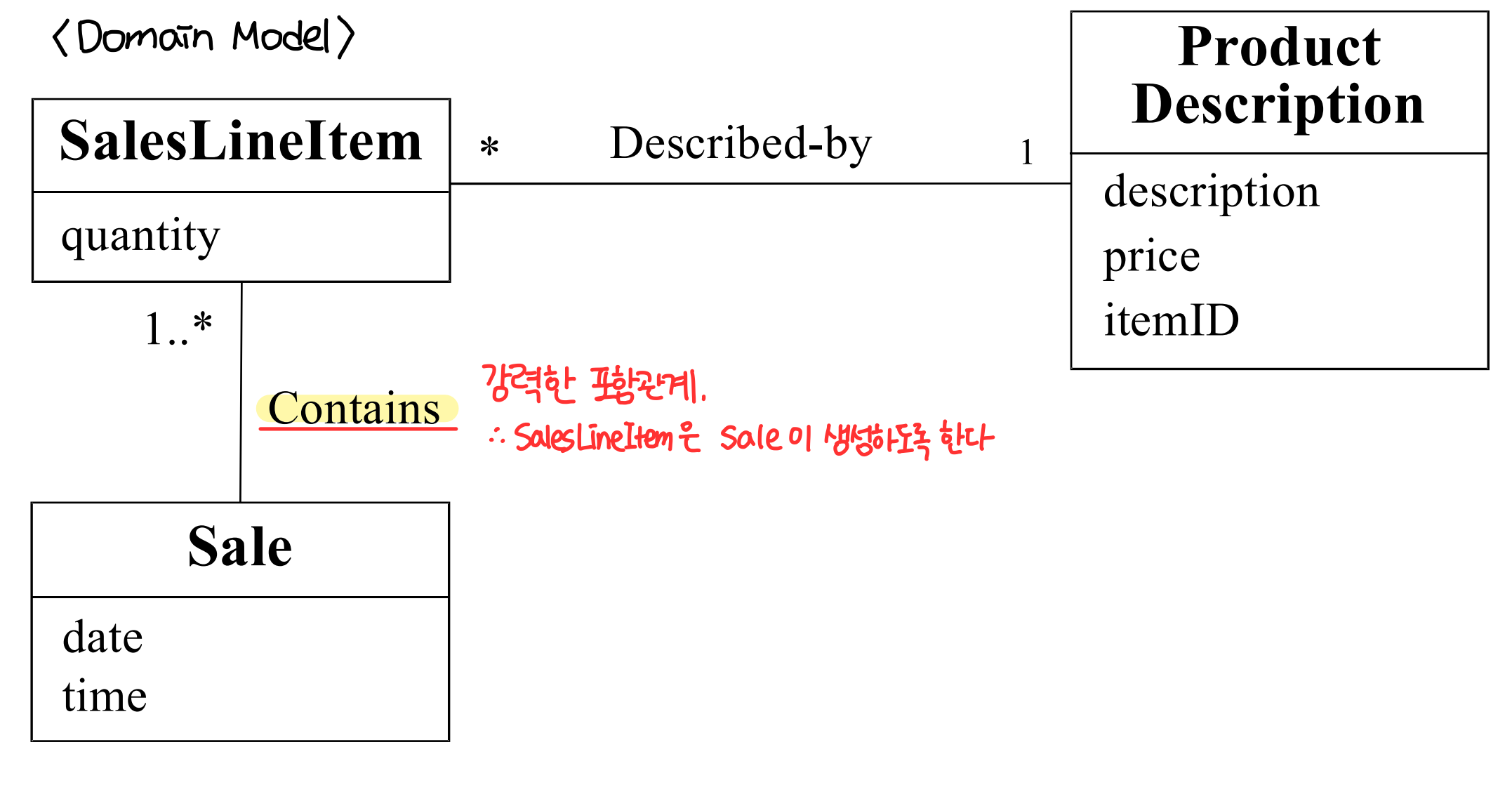
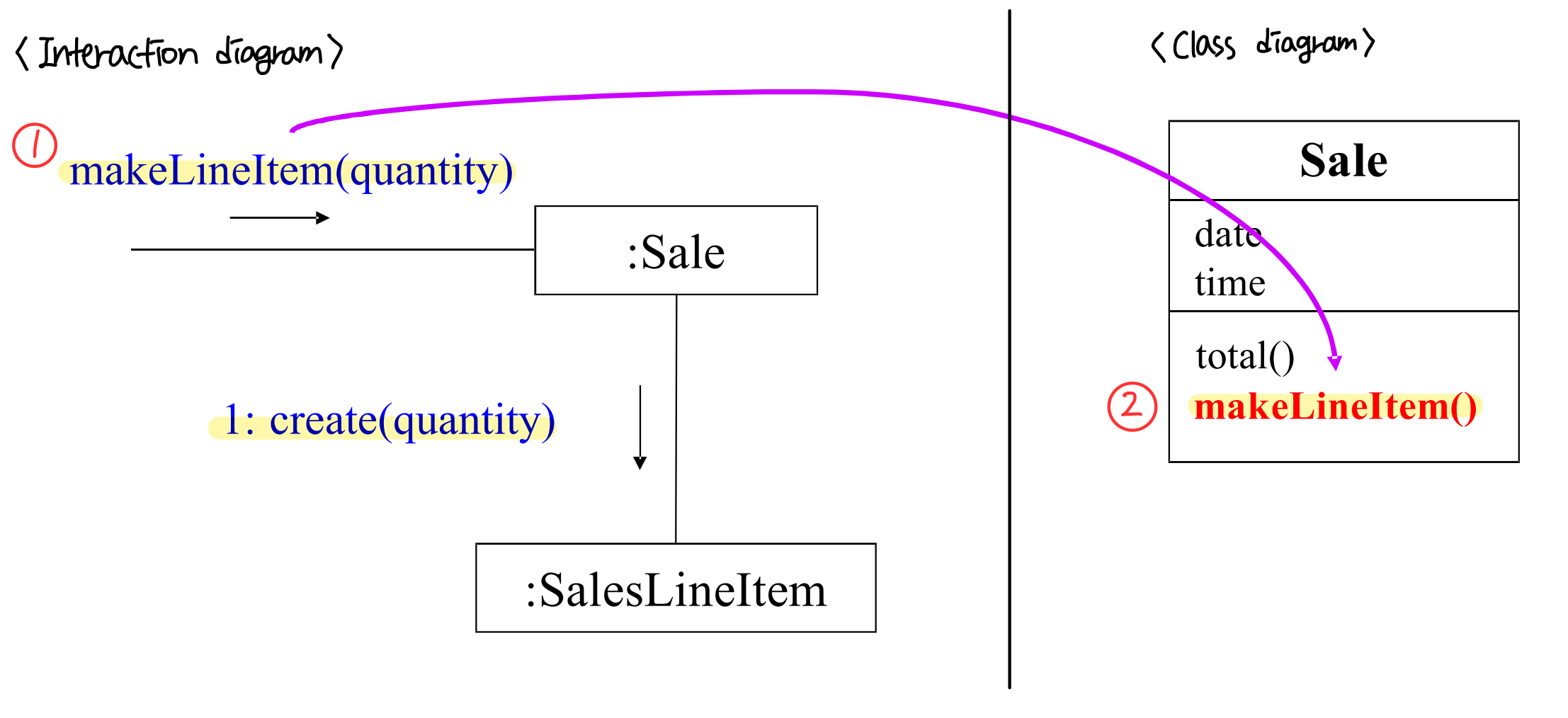
- B 는 인스턴스 A 를 만드는 역할을 한다. 만약 새로 C 라는 클래스가 A 의 인스턴스를 생성하면, dependency 를 가지게 된다. 이처럼 A 에 대해 dependency 를 가지는 것이 늘어나는 건 좋지 않기 때문에 A 를 생성하는 클래스를 지정해준다.
- Problem
: 누가 새로운 instance 를 생성해야하는 responsiblity 를 가져야 하는가?
- Solution
: 다음 중 하나가 참일 경우, 클래스 B 가 클래스 A 를 생성할 responsiblity 를 가진다.- B aggregates A
- B contains A
- B records instances of A
- B closely uses A
- B has the initialization data the will be passed to A When it is created. (B는 생성될 때 A로 전달될 초기화 데이터를 가지고 있다.)
- Example : SalesLineItem 의 instance 는 누가 만들것인가?
3️⃣Low Coupling (클래스간)
Coupling : 클래스가 다른 클래스에 dependencies 되는 정도
// X 는 Y 에 대해 dependency 를 가짐 | [X] ---> [Y] class X extends Y { // (1) Y y; // (2) field Y foo(Y y) { // (3) return, (4) parameter Y y; // (5) local variable } }(1-1) typeX 가 typeY 의 subclass 이다.
(1-2) typeX 가 (interface) Y 를 구현한다.
(2) typeX 가 typeY 를 instance variable 로 가진다.
(3) typeX 의 method 가 typeY 를 return value 로 가진다.
(4) typeX 의 method 가 typeY 를 parameter 로 가진다.
(5) typeX 가 typeY 인 local variable 을 가진다.
- Low coupling : more independent, more reusable => higher productivity
- Problem
: 낮은 dependency 와 증가된 reuse 를 지원하는 방법이 무엇인가?
- Solution
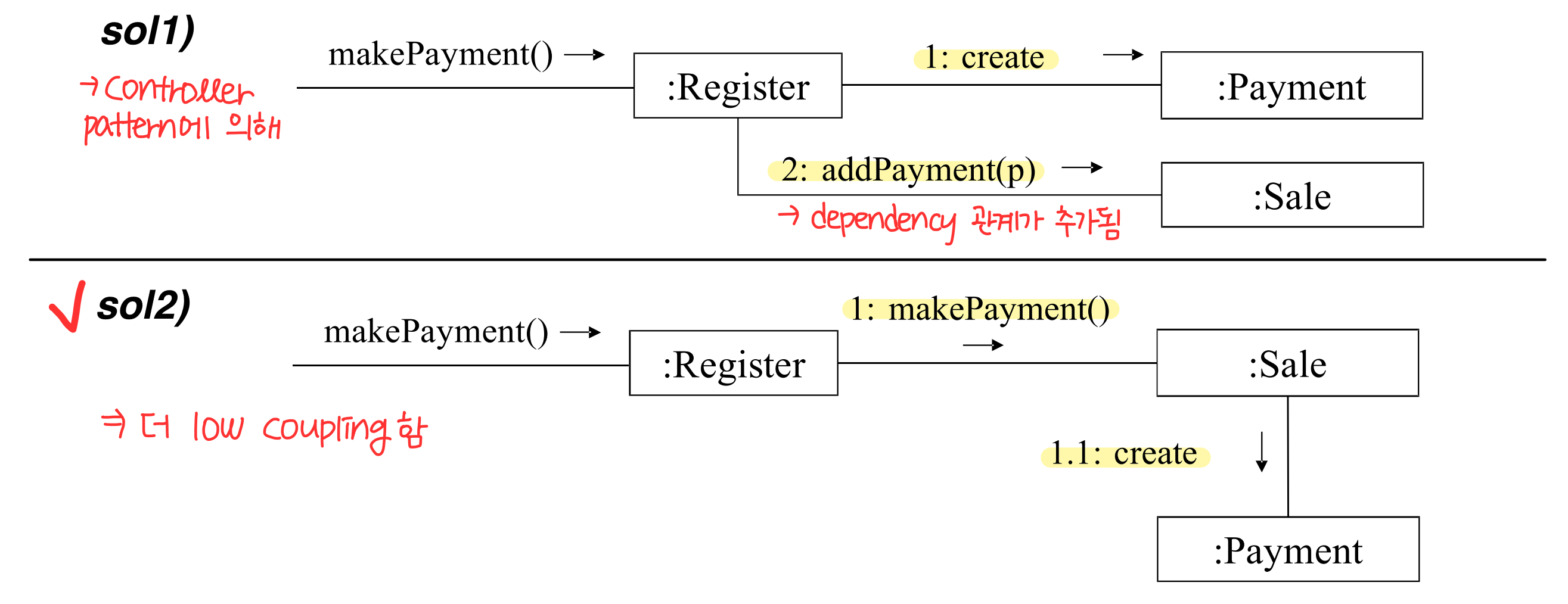
: coupling 이 낮게 유지되도록 responsibilities 를 할당한다. - Example : Payment 를 생성하고, Sale 과 associate 해야한다. 누가 이 responsibities 를 가질것인가?
4️⃣High Cohesion (operation간)
operation 끼리 얼마나 연관된 responsibility 를 가지는가
low cohesion : 관련없는 operation(responsibility)가 모여있다.
- comprehend(이해), reuse(재사용), maintain(유지) 하기 어렵고, delicate(연약)하다.
- Problem
: complexity 를 manageable 하게 유지하는 방법
- Solution
: 높은 cohesion 을 가지도록 responsibility 를 부여한다. - Example : Payment 를 생성하고, Sale 과 associate 해야한다. 누가 이 responsibities 를 가질것인가?
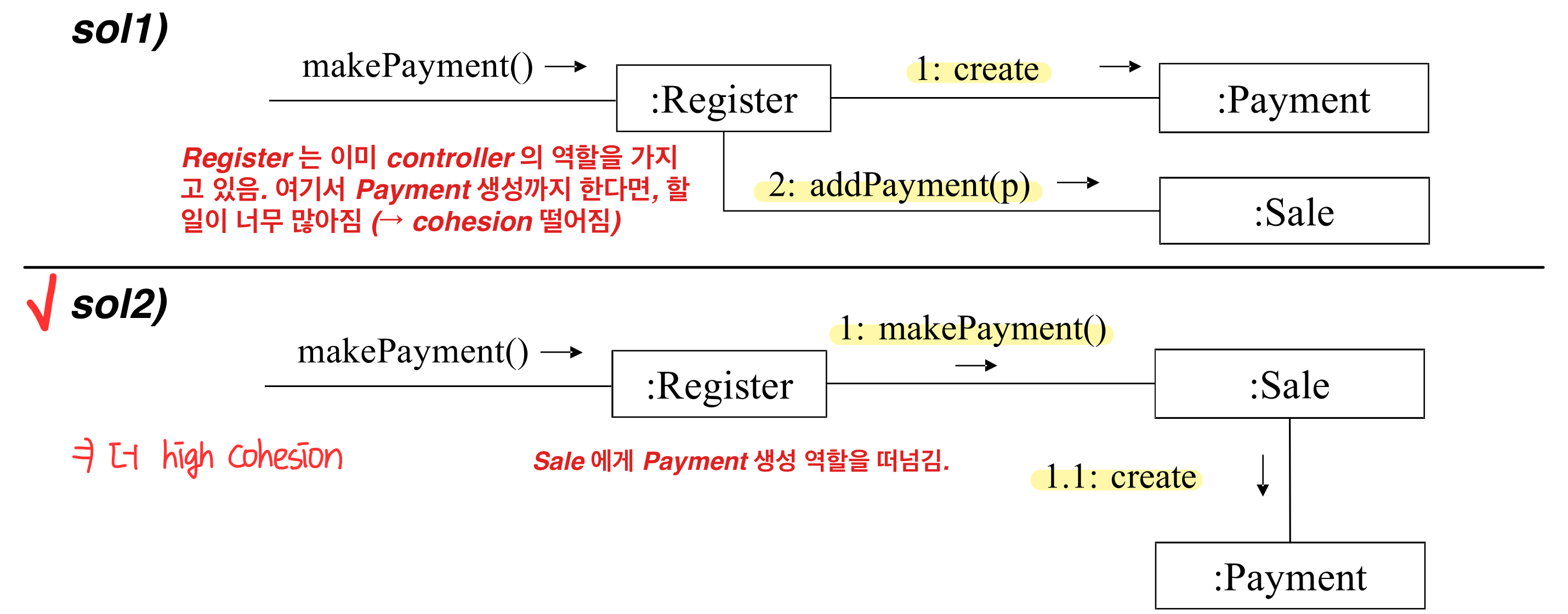
High Cohesion & Low Coupling : evaluation patterns
- 모든 설계 중에 명심해야 하는 것이며, design decision 을 평가할 때 적용하는 evaluation pattern 이다.
5️⃣Controller
아키텍처 설계.
아주 simple 한 경우를 제외하고, controller 는 맞이하는 역할만 해야함.
- 실제 operation 이 보장해야하는 조건을 만족하기 위해서는 그것을 가장 잘 하는 다른 object 에게 떠넘겨야함.
- Problem
: 누가 system event 를 맞이(handling)할것인가?
Solution
: 다음 중 하나 또는 하나 이상을 나타내는 클래스에 responsibility 를 assign 한다.- facade controller : 시스템 전체를 나타낸다.
- use-case controoler / session controller : artificial handler 를 나타낸다. → use-case 별로 하나씩 생성될 수 있다.
controller 는 non-GUI object 이다.
Bloated Cntrollers : facade controller 가 (처리하는 operation 이 많아서) 너무 fat 해졌을 때, use-case controller 를 병행해서 여러개의 controller 를 쓸 수 있다.
[Typical Layered Architecture]
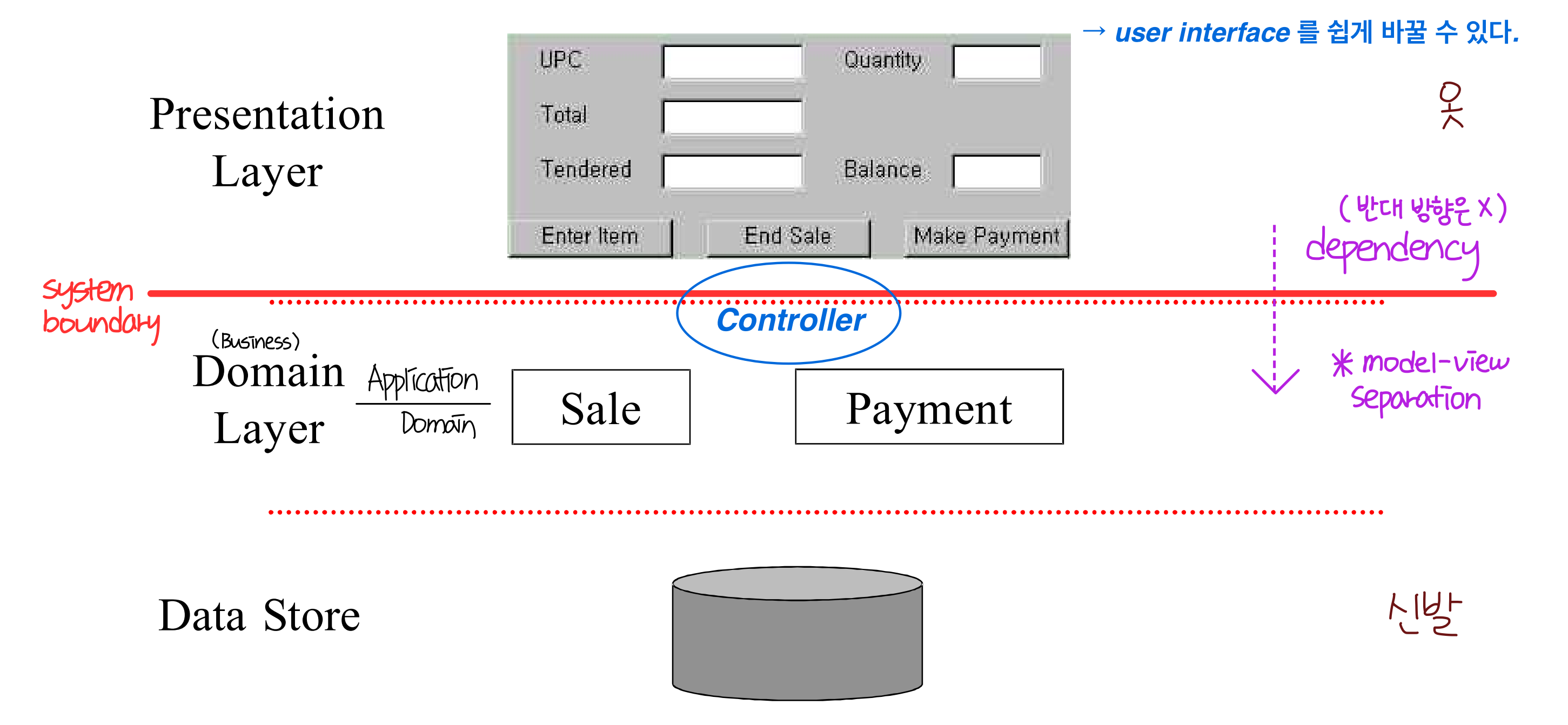
- presentation layer 는 system event 를 처리할 책임이 없어야함.
= domain logic 을 맡겨서는 안된다.
→ presentation layer 는 나중에 바뀔 수 있는 가능성이 충분히 있으므로, presentation layer 에 대한 dependency 를 가지게 해서는 안된다.
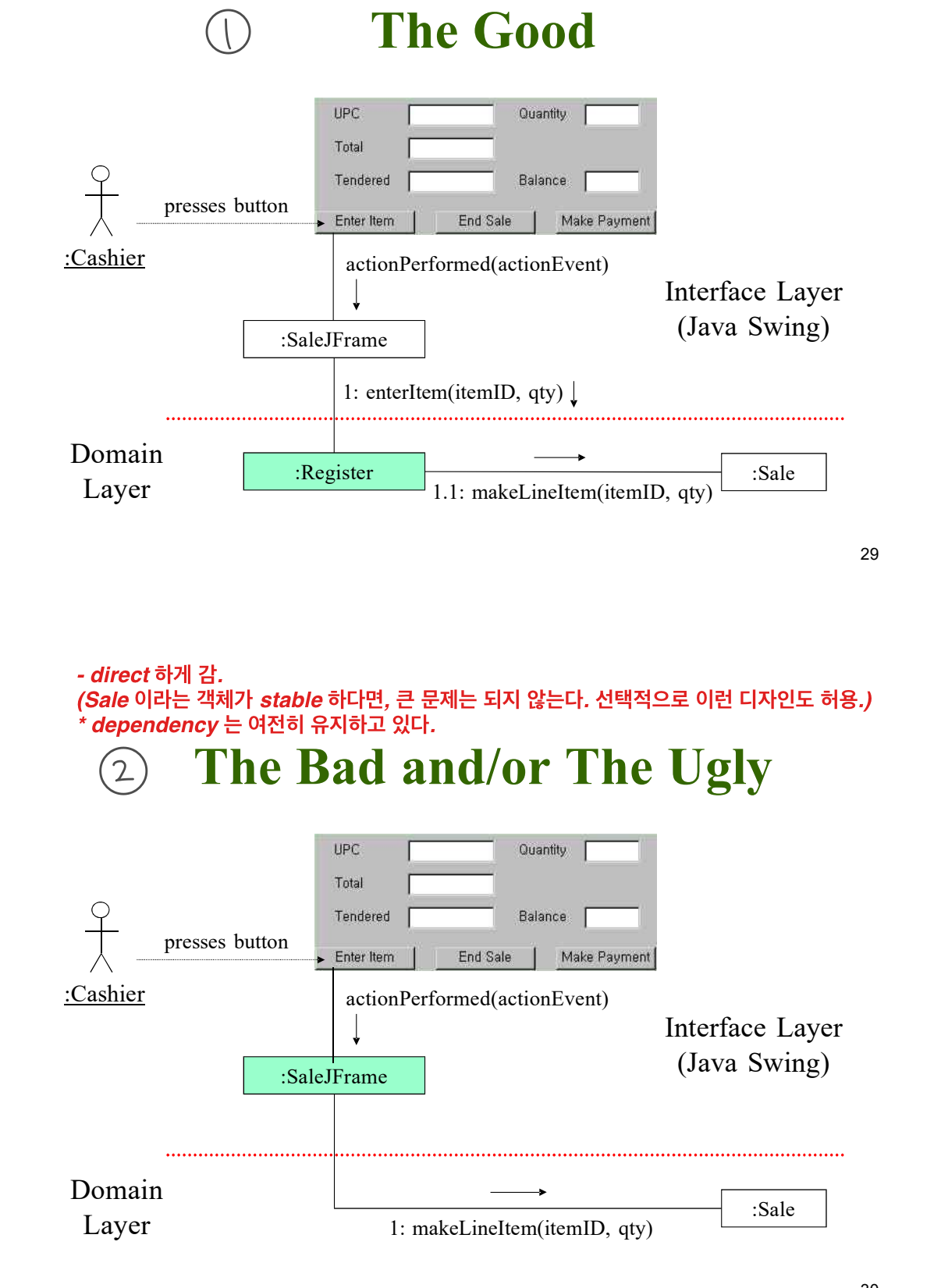
In Our Example
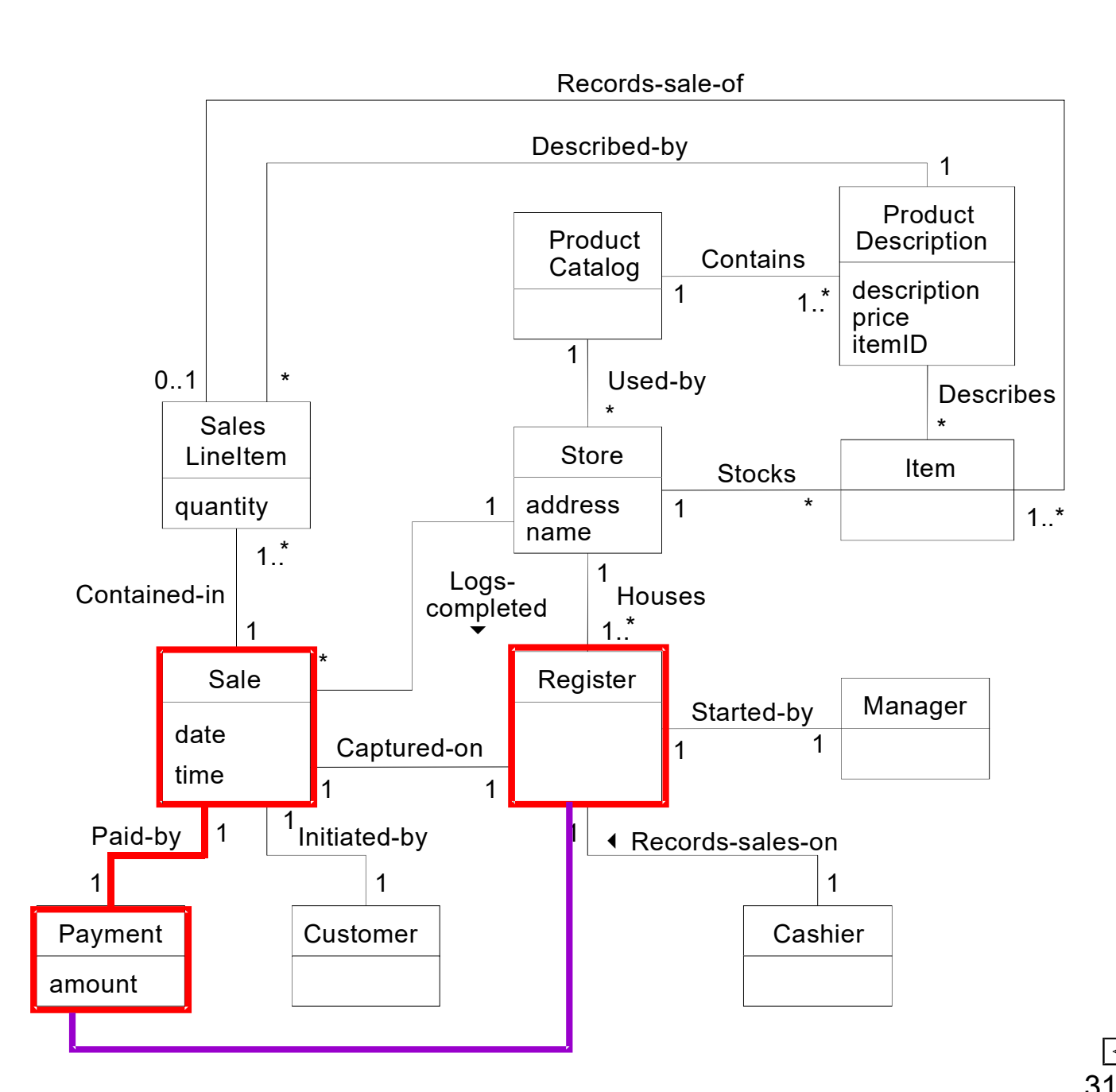
6️⃣Polymorphism
- type 에 따라 대처방법을 만들지마라.
7️⃣Pure Fabrication
- domain model 에 없는 오브젝트이더라도, 필요시 인위적으로 만들어 소프트웨어 클래스에 사용한다
8️⃣Indirection
- 직접적인 coupling 를 피하기위한 방법.
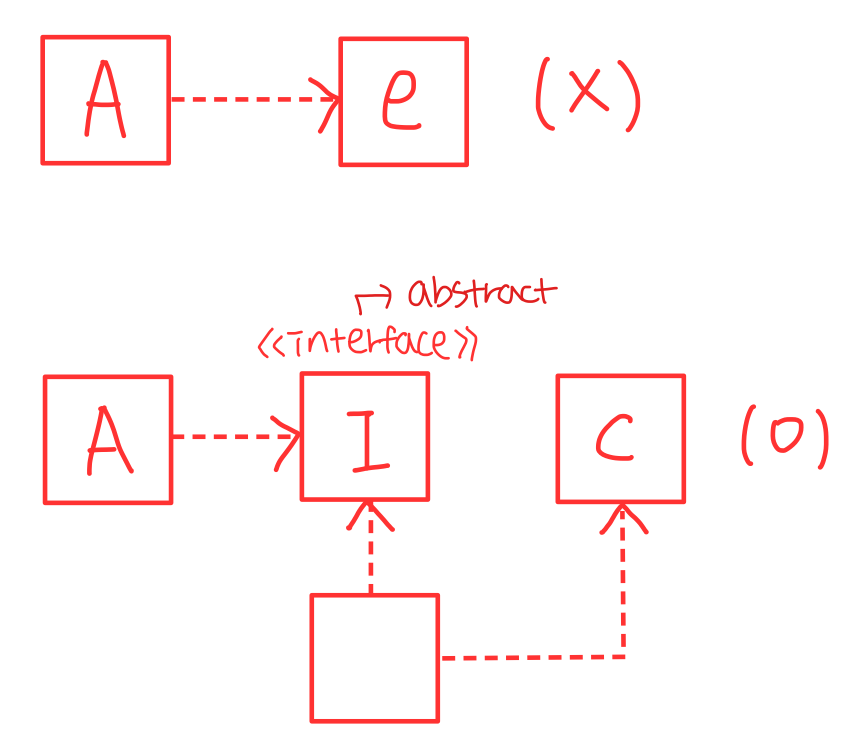
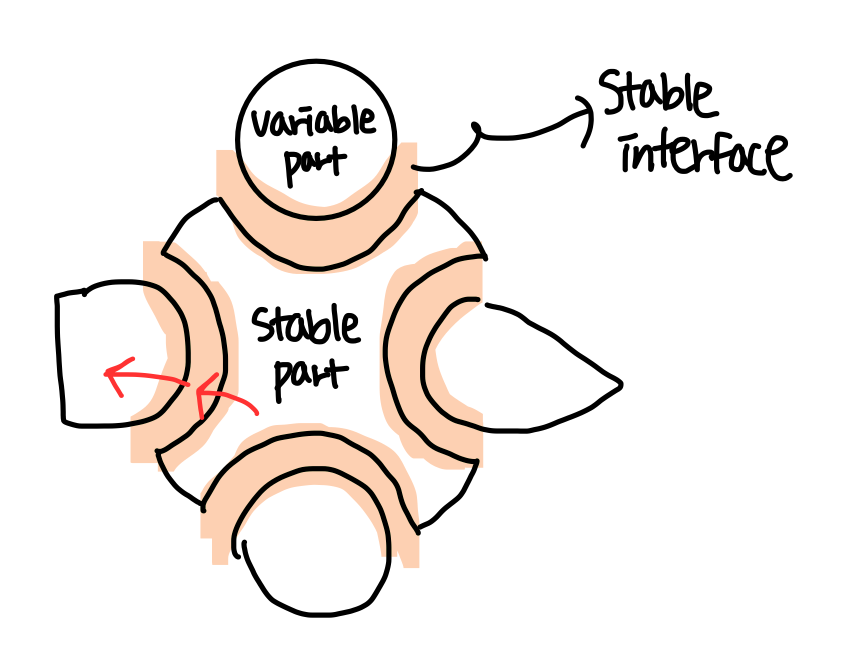
9️⃣Protected Variations
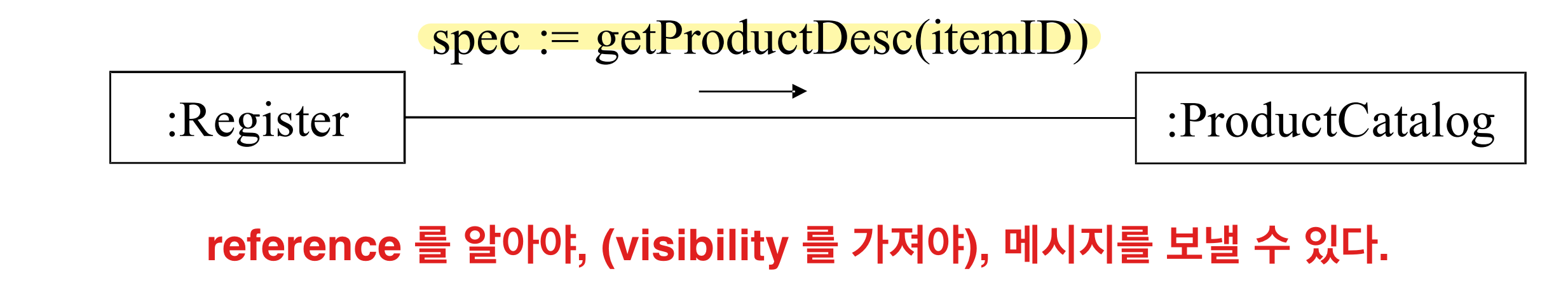
Visibility
- A 가 B 에게 메시지를 보낼 수 있다면 = B be visible to A. (b가 a에게 보여야함)
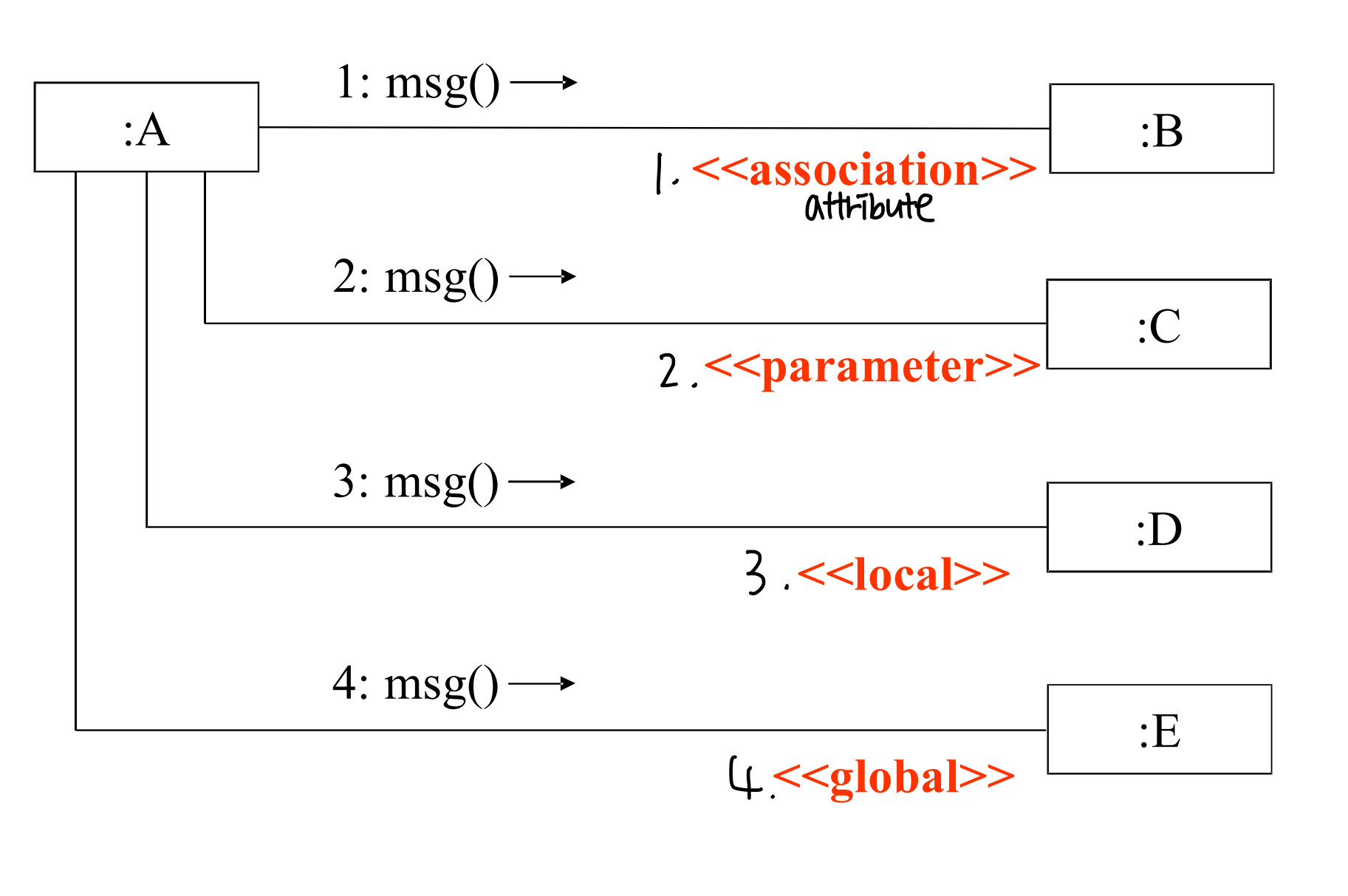
(1) Attribute visibility
- B 는 A 의 attribute 이다.
(2) Parameter visibility
- B 는 A 의 parameter 이다. (일시적)
(3) Local visibility
- B 는 A 의 메소드에 의해 선언되는 오브젝트이다. (일시적)
(4) Global visibility
+Class Diagram
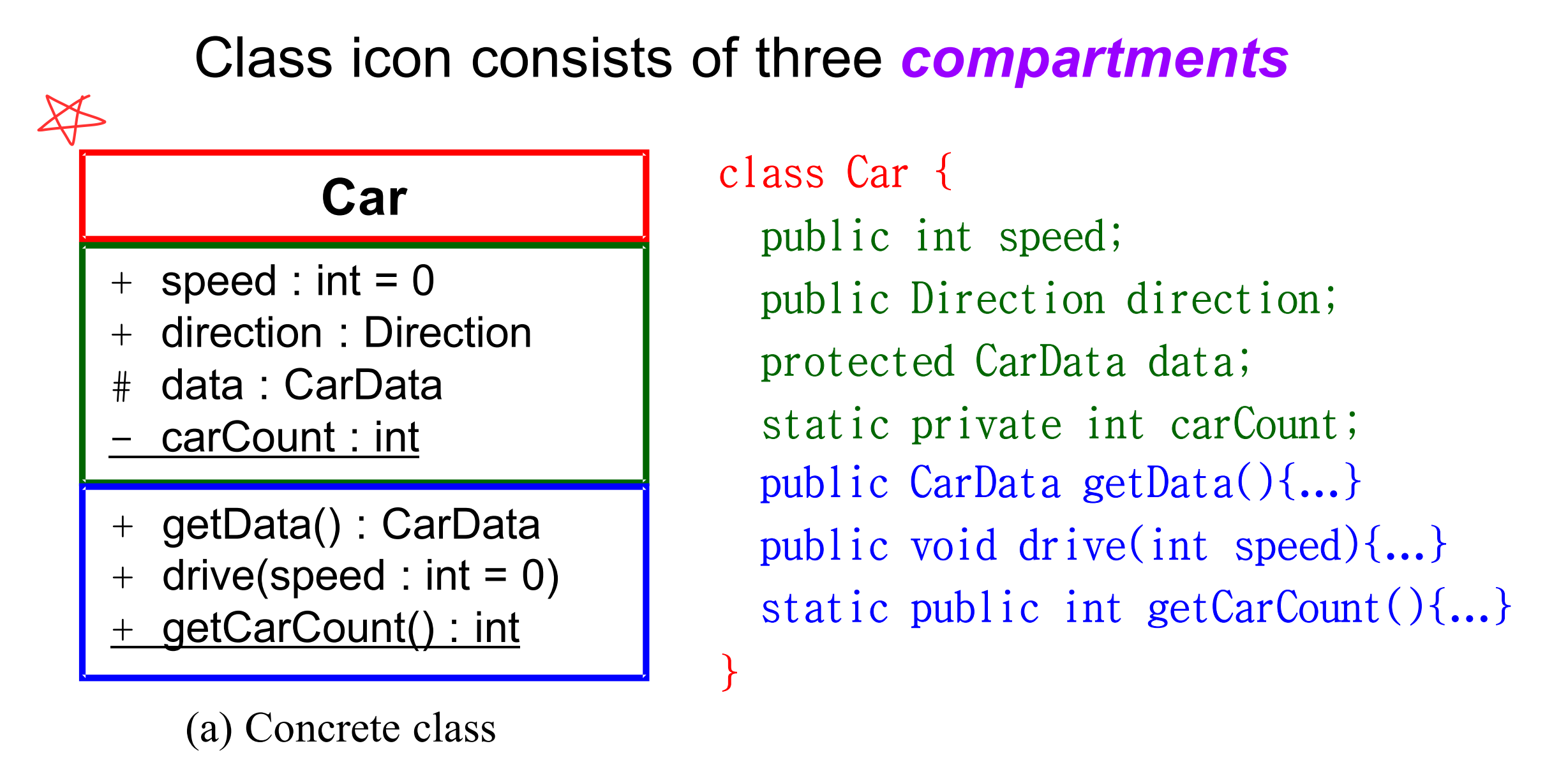
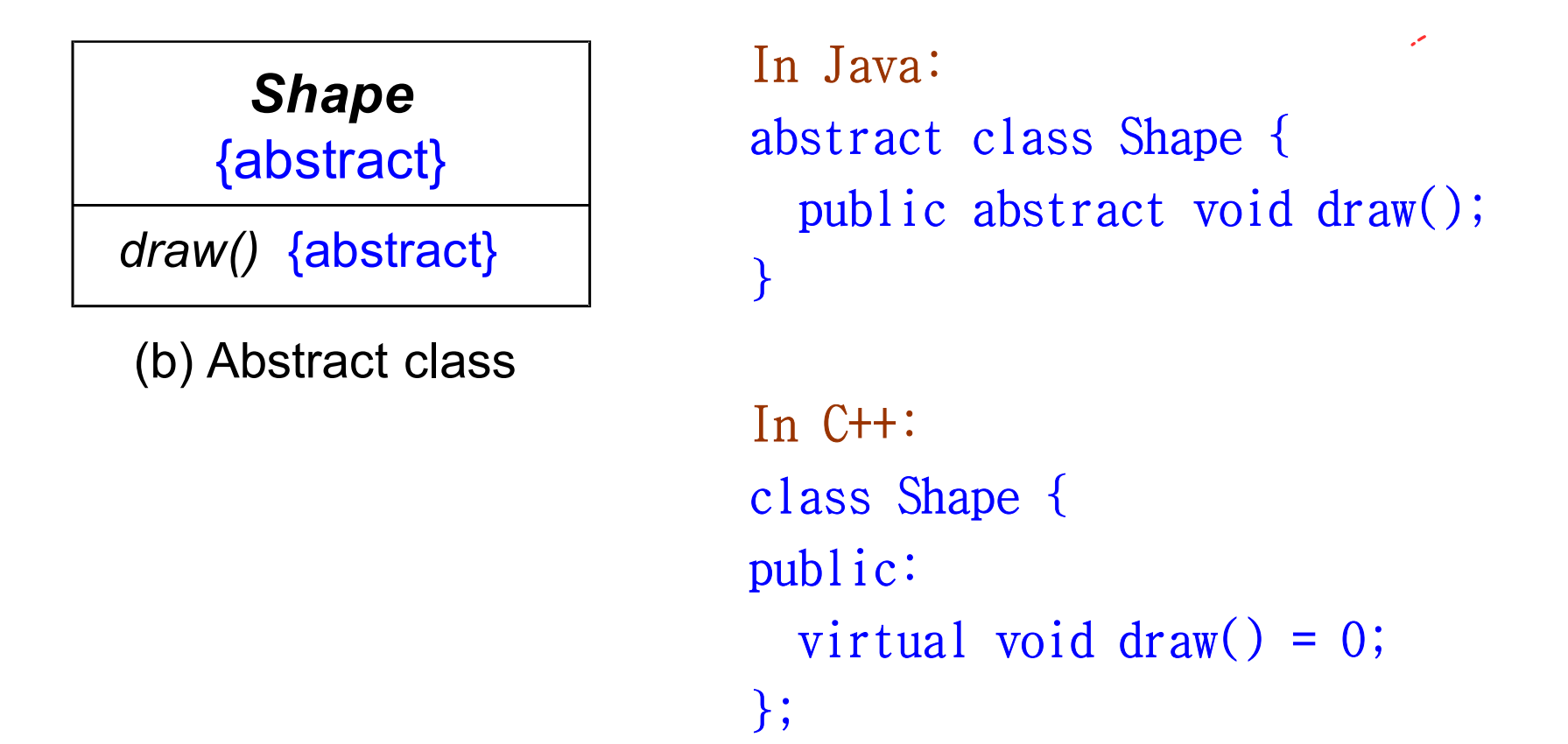
Example
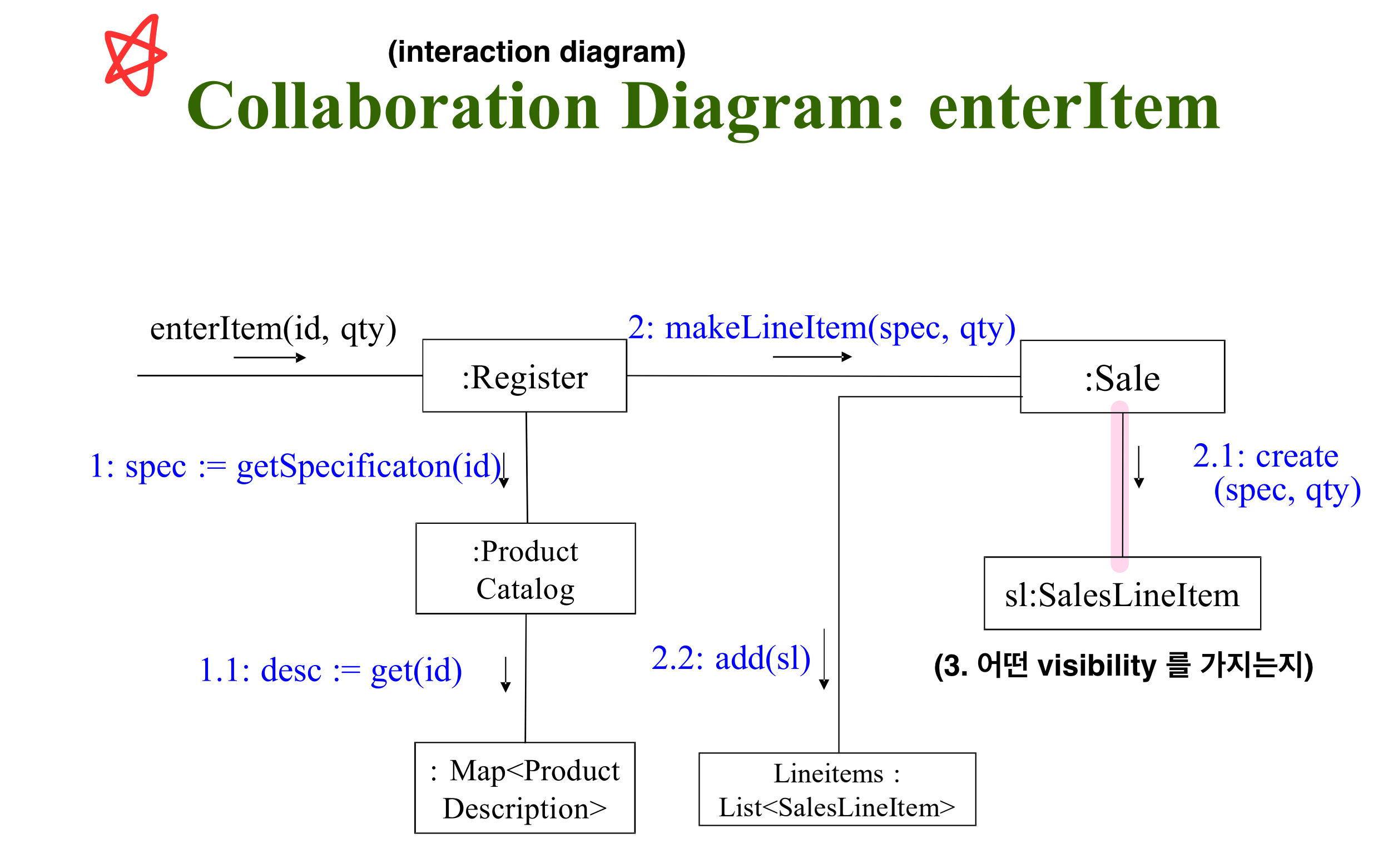
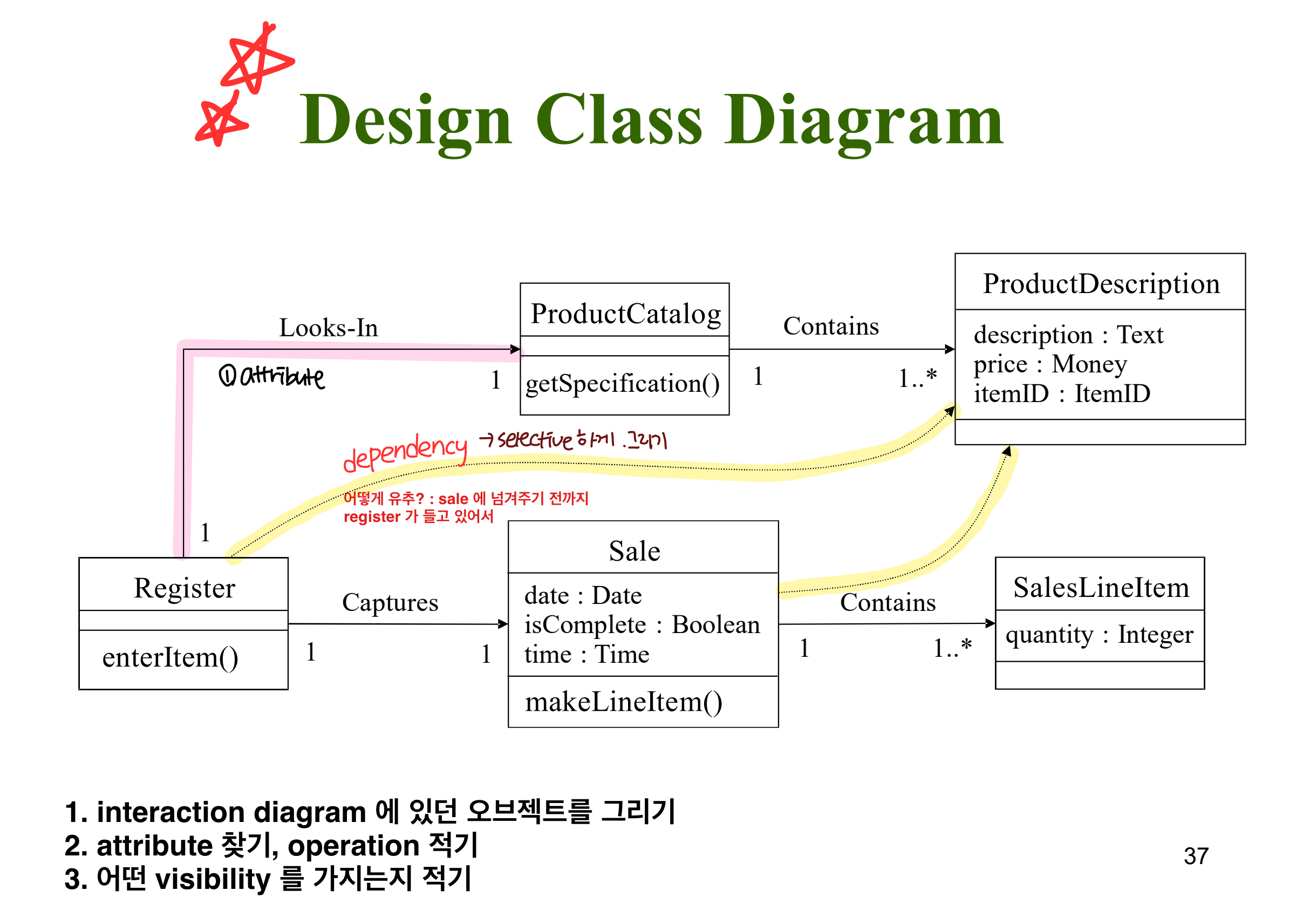
+Organizing Use Cases
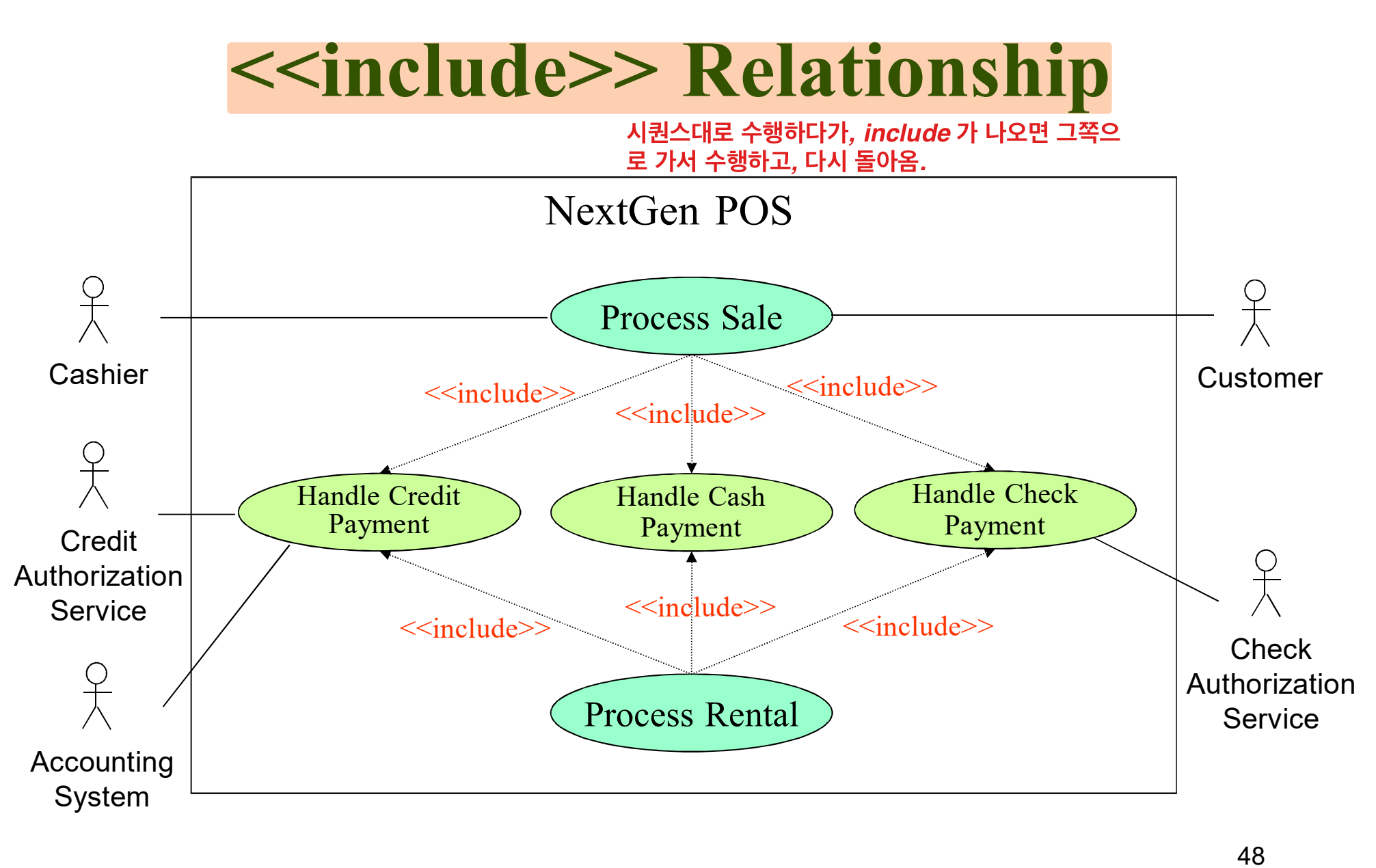
+Domain Model
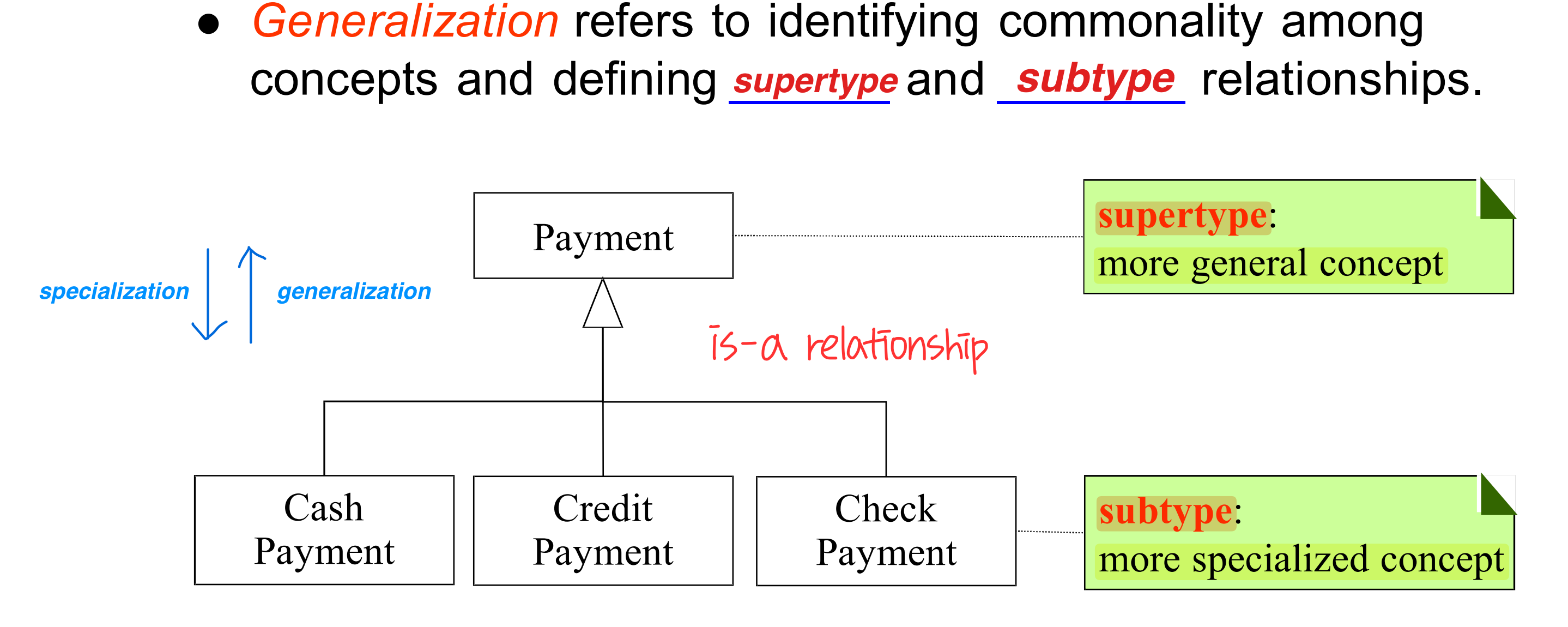
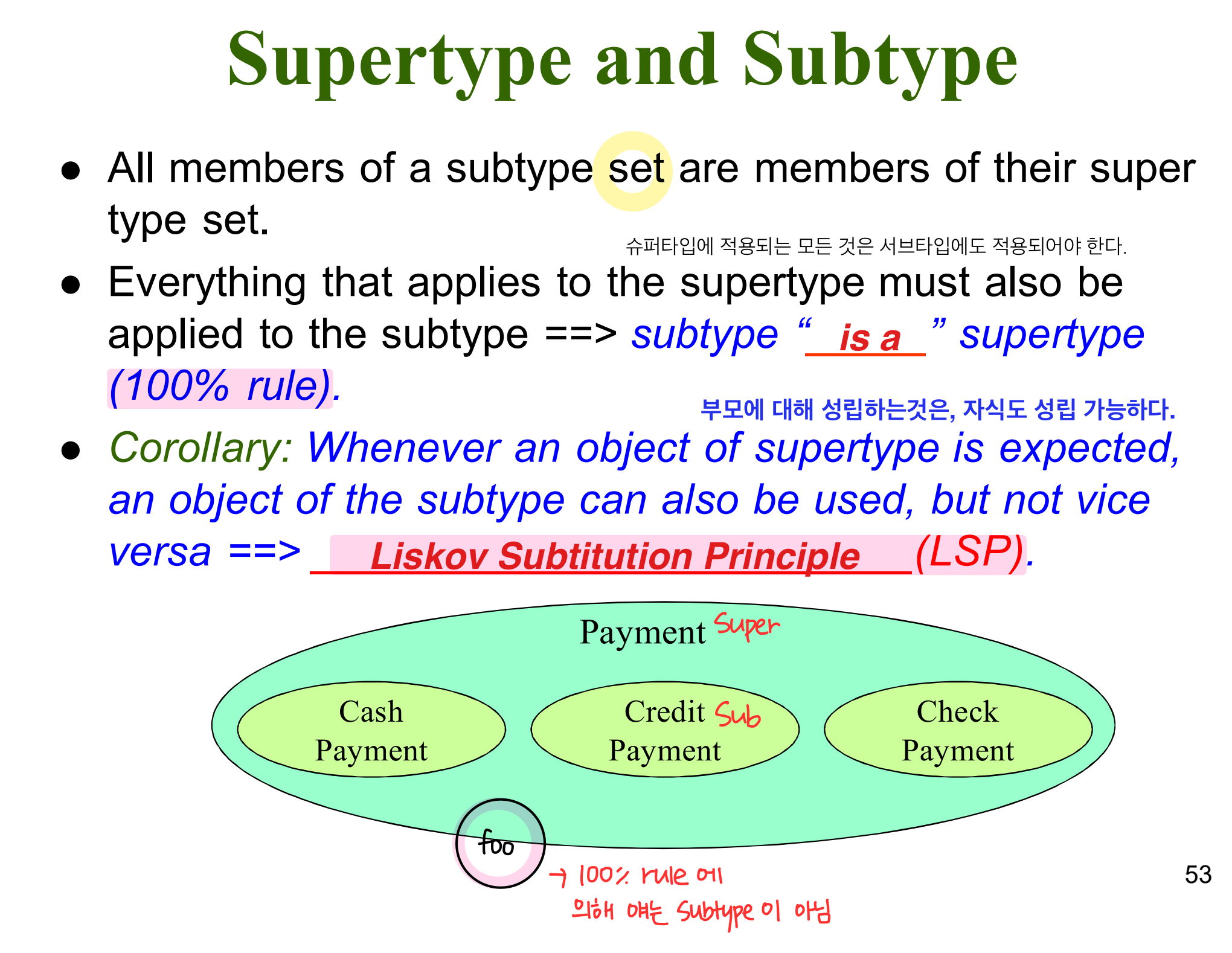
Generalization / Specialization
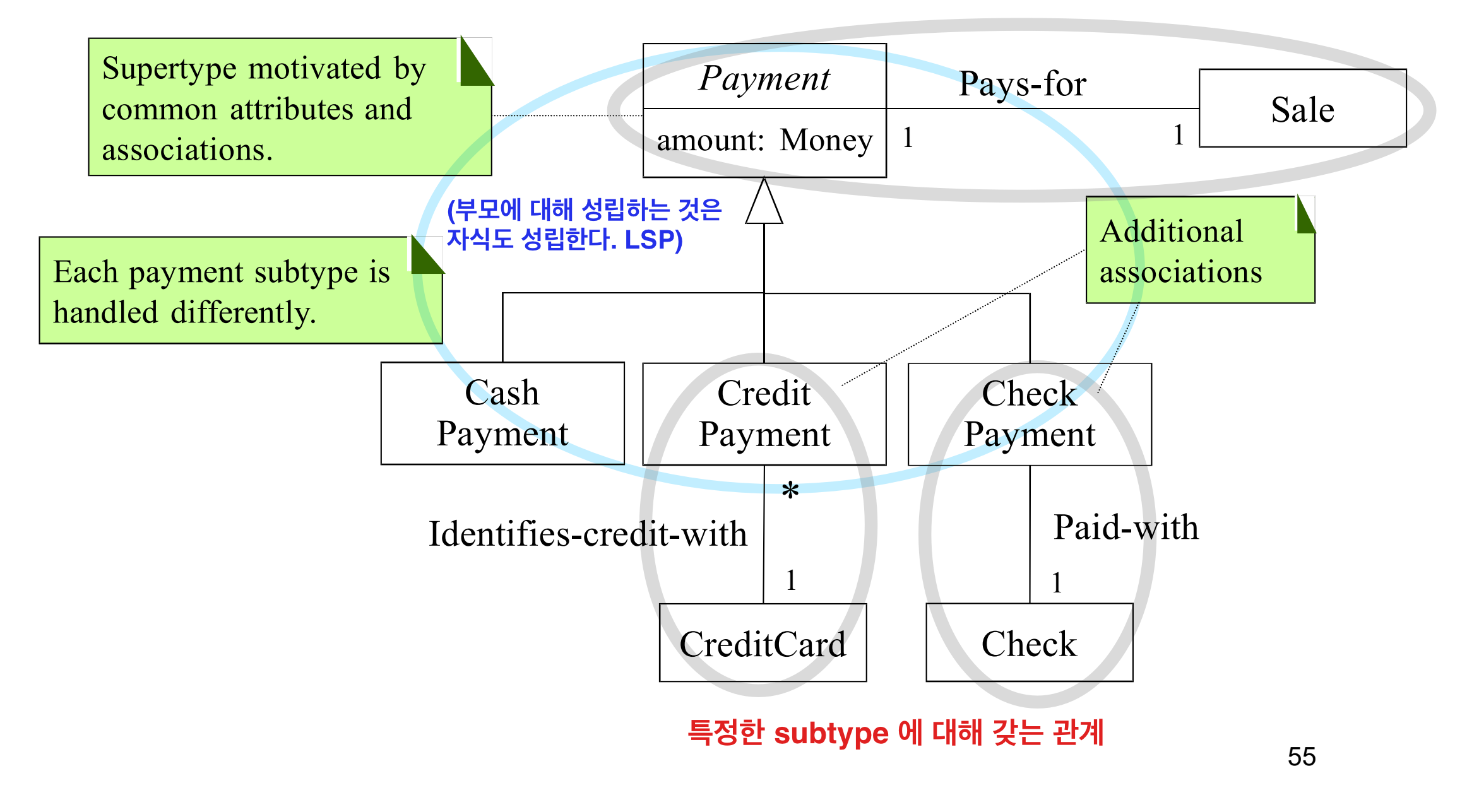
Example
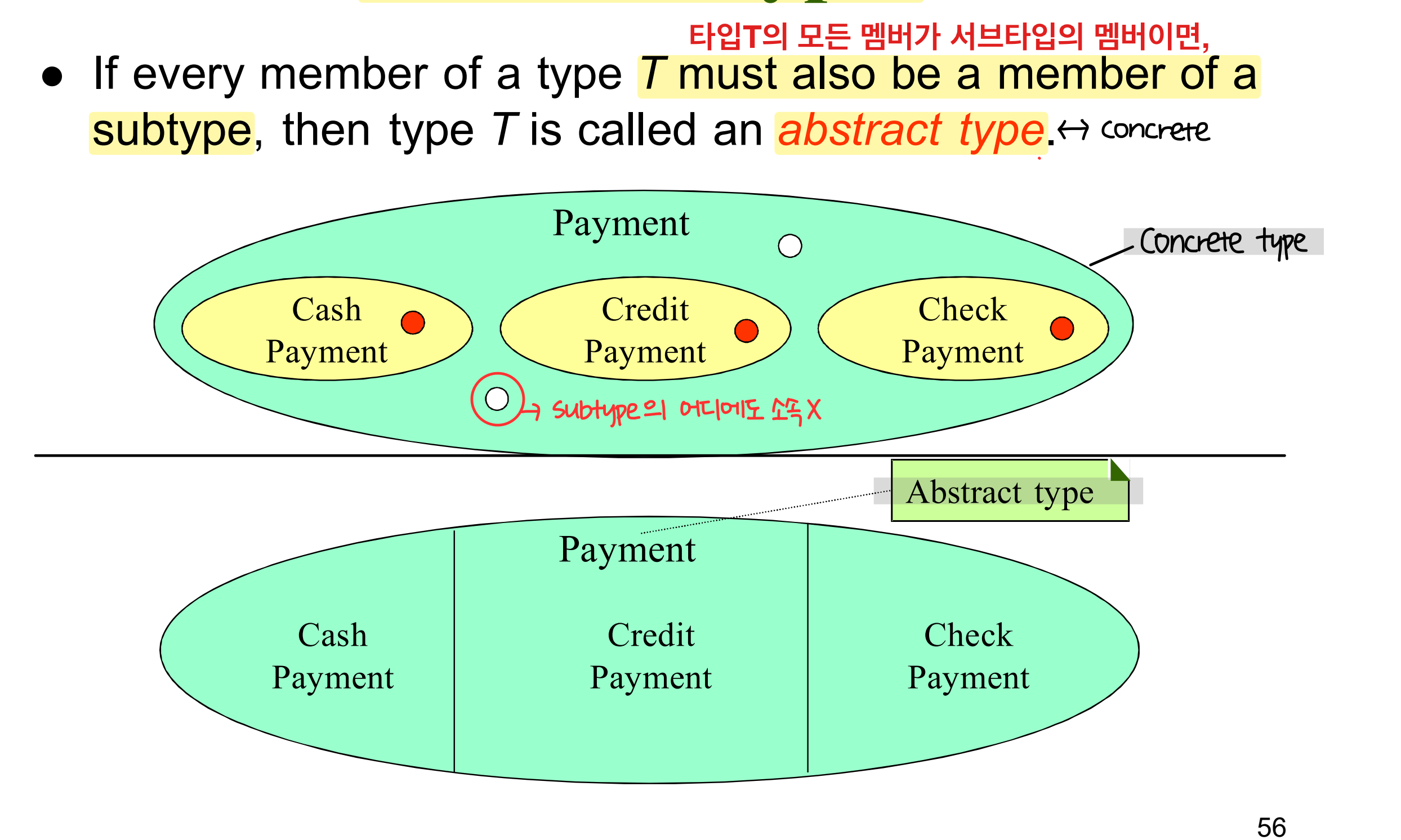
Abstract Types
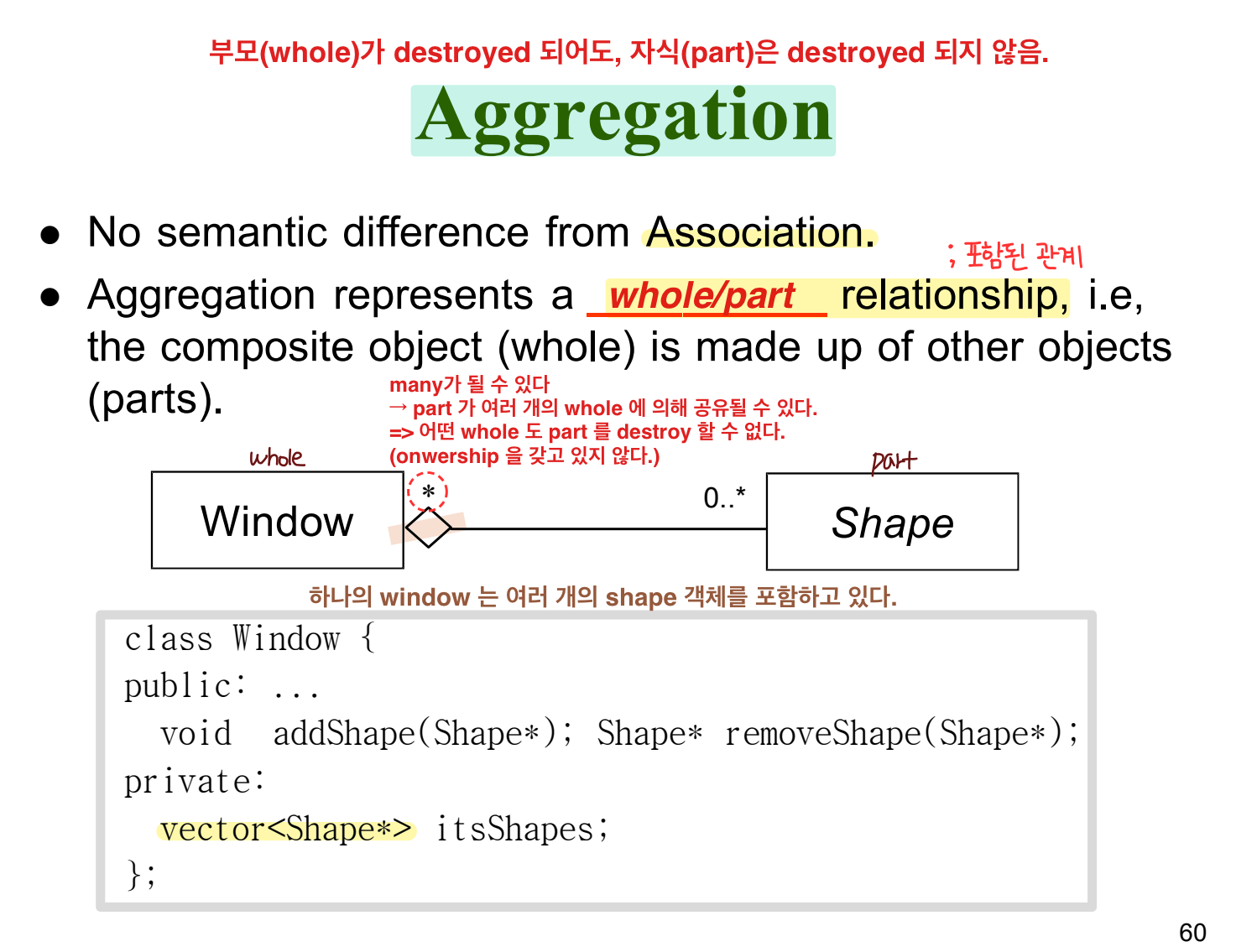
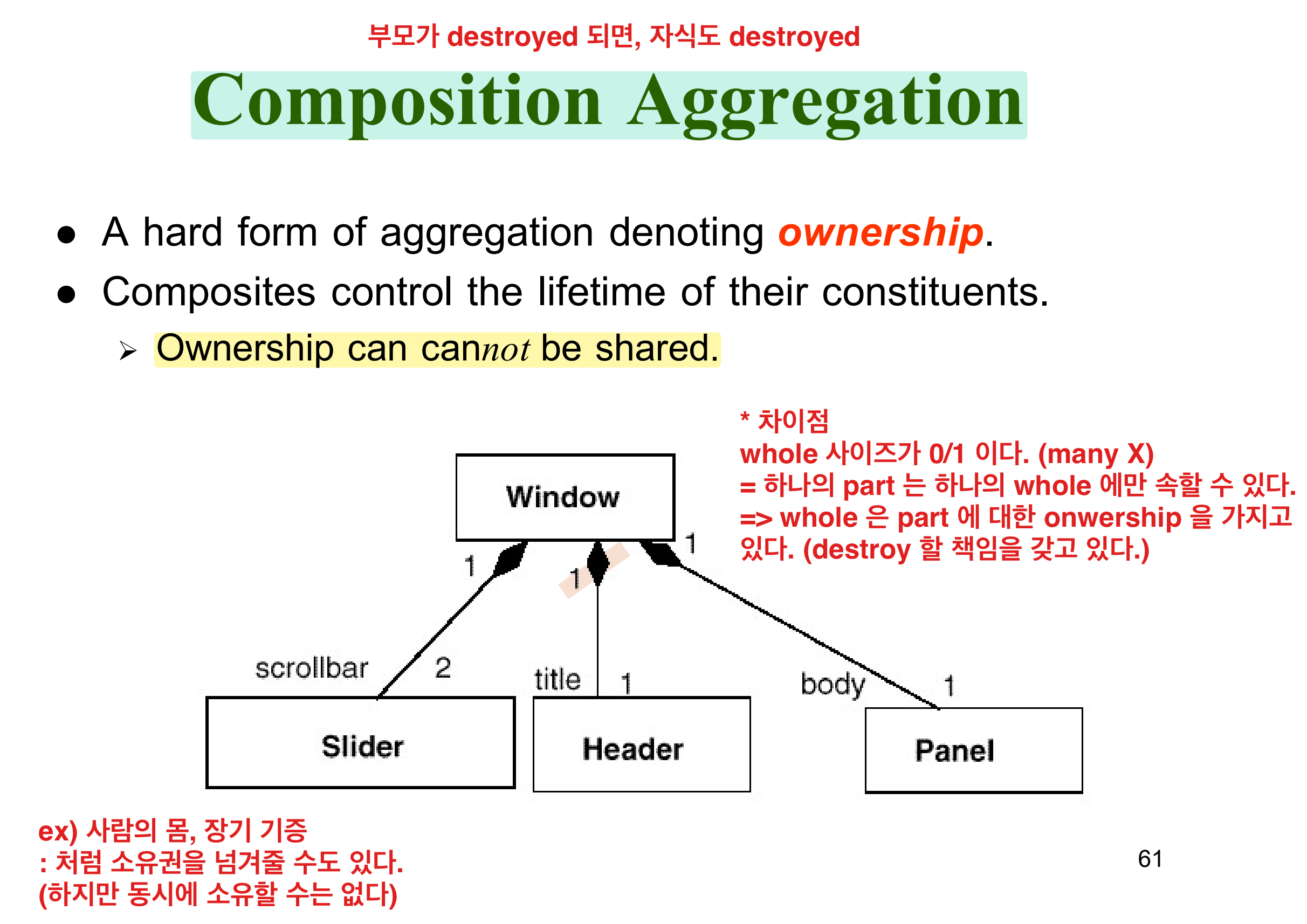
aggregation & composition aggregation relationships
| Aggregation | Composition Aggregation |
|---|---|
| 부모가 없어도, 자식은 산다. | 부모가 없으면, 자식도 죽는다 |
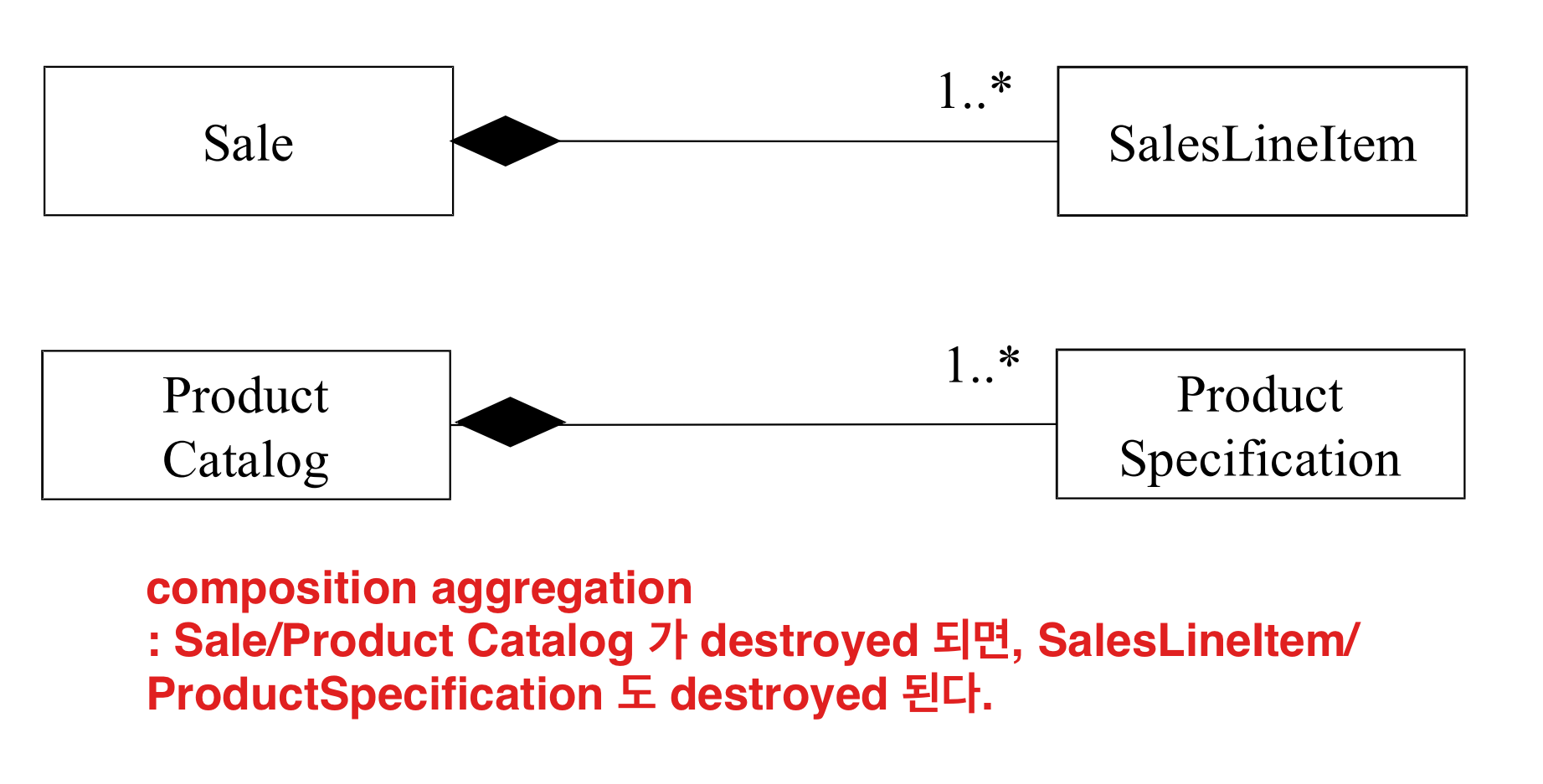
Example
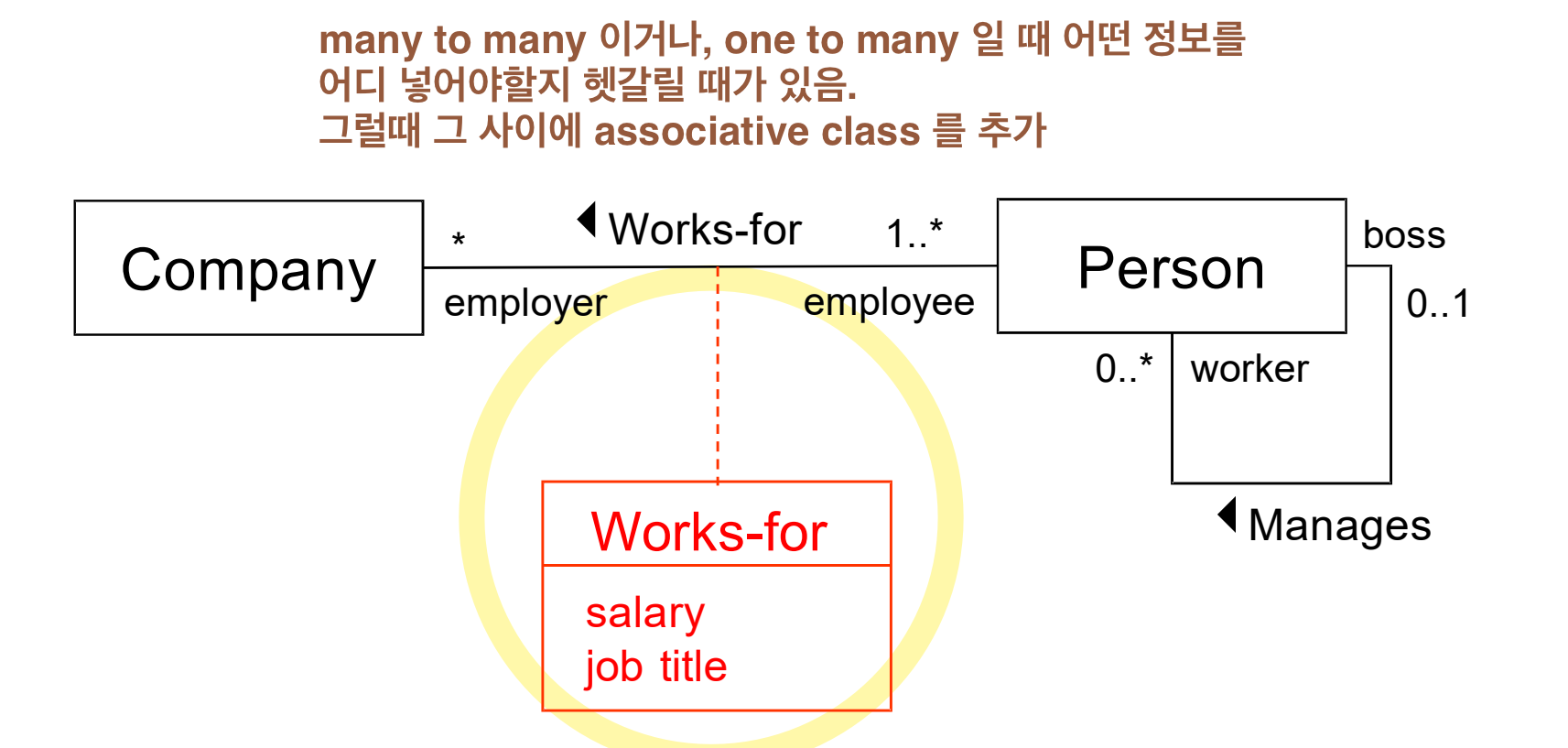
Associative Type
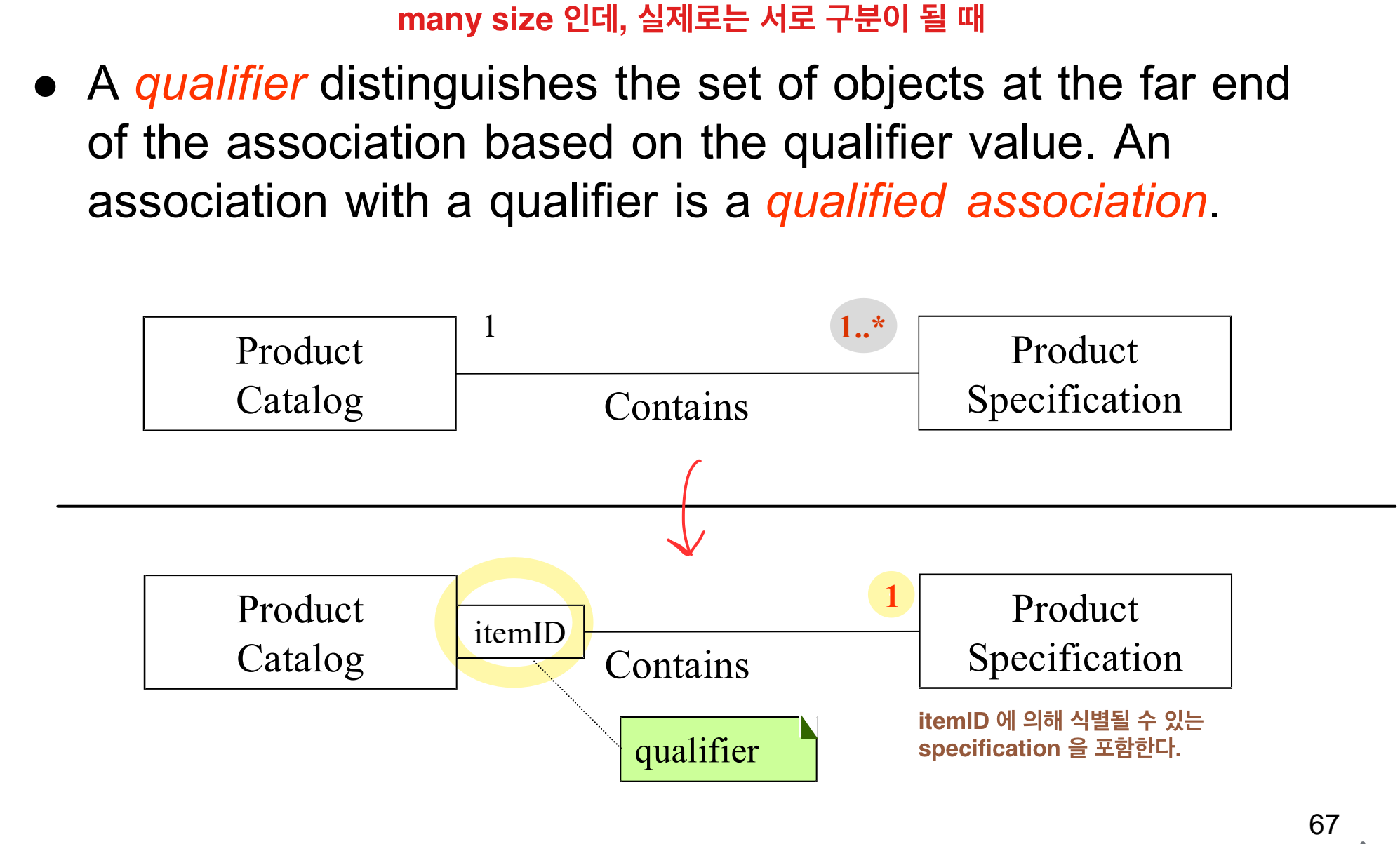
Qualified Associations
Dependency
- 일시적 관계를 말함
- 모든 structure association 은 dependency 이다.
'* CS > 객체지향개발론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [객체지향개발론] 07 Sequence Diagram (0) | 2023.08.08 |
|---|---|
| [객체지향개발론] 06 Domain Model(2) and Class Diagram (0) | 2023.08.06 |
| [객체지향개발론] 05 SSD and Domain Model(1) (0) | 2023.08.05 |
| [객체지향개발론] 04 Use Case (0) | 2023.08.04 |
| [객체지향개발론] UML (0) | 2023.08.02 |