[객체지향개발론] 06 Domain Model(2) and Class Diagram
Domain Model(2)
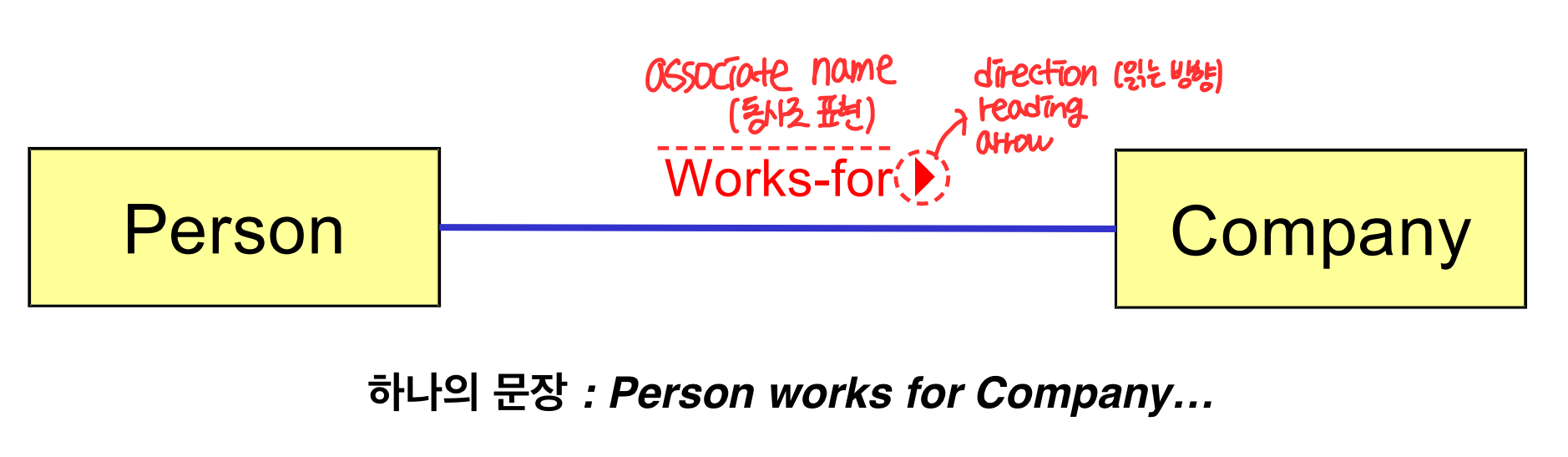
📌Association
- ⭐️Structural relationship : conceptual class 간의 connection 을 나타낸다.
- 한 번 연관관계가 맺어지면 어느정도 기간을 유지한다.
- analysis phase 에선, data flow 의미가 아닌 analytical 적인 의미를 가진다.
- 구현에 필요하지 않은 association 이나, 구현 중 필요한 association 이 누락될 수 있다. 이런 것을 발견하면 업데이트 해주어야 한다.
- design phase 에선, 주로 association 은 class 의 attribute 로 표현된다.
- conceptual class 를 찾아낼 때, conceptual category list 에서 찾아내듯이, association 은 common associations list 에서 찾을 수 있다.
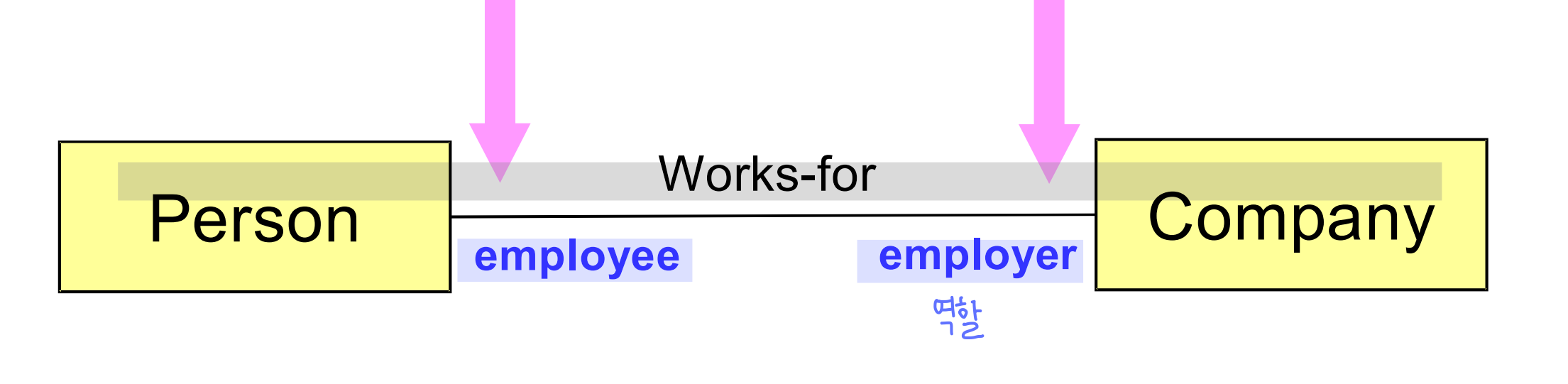
Role Name
- association 끝에 그 association 에서 수행하는 역할을 설명한다.
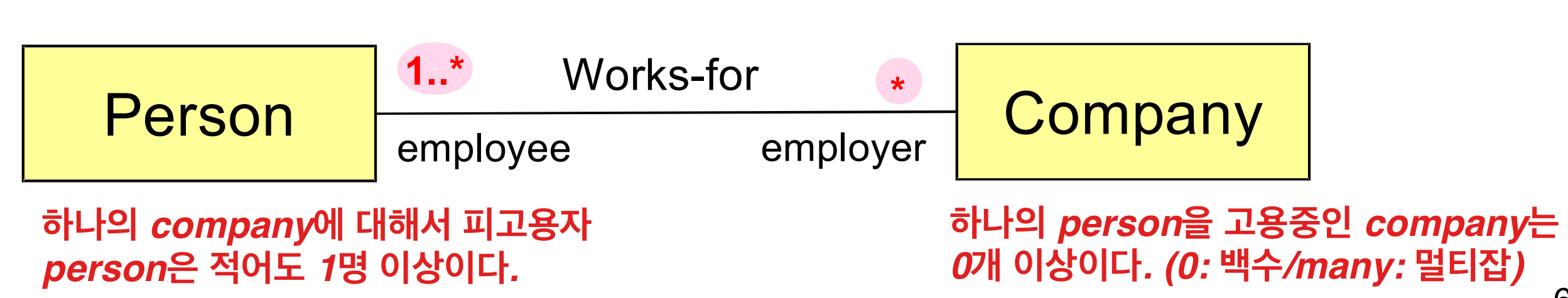
Multiplicity (Cardinality)
: 반대쪽에 대해서 동시에 가질 수 있는 역할의 수
| 표기 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| * / 0..* | Zero to many |
| 1..* | One to many |
| 0..1 | Zero or One |
| 1 | One and only one |
| n..m | Where n and m are any two integers |
 |
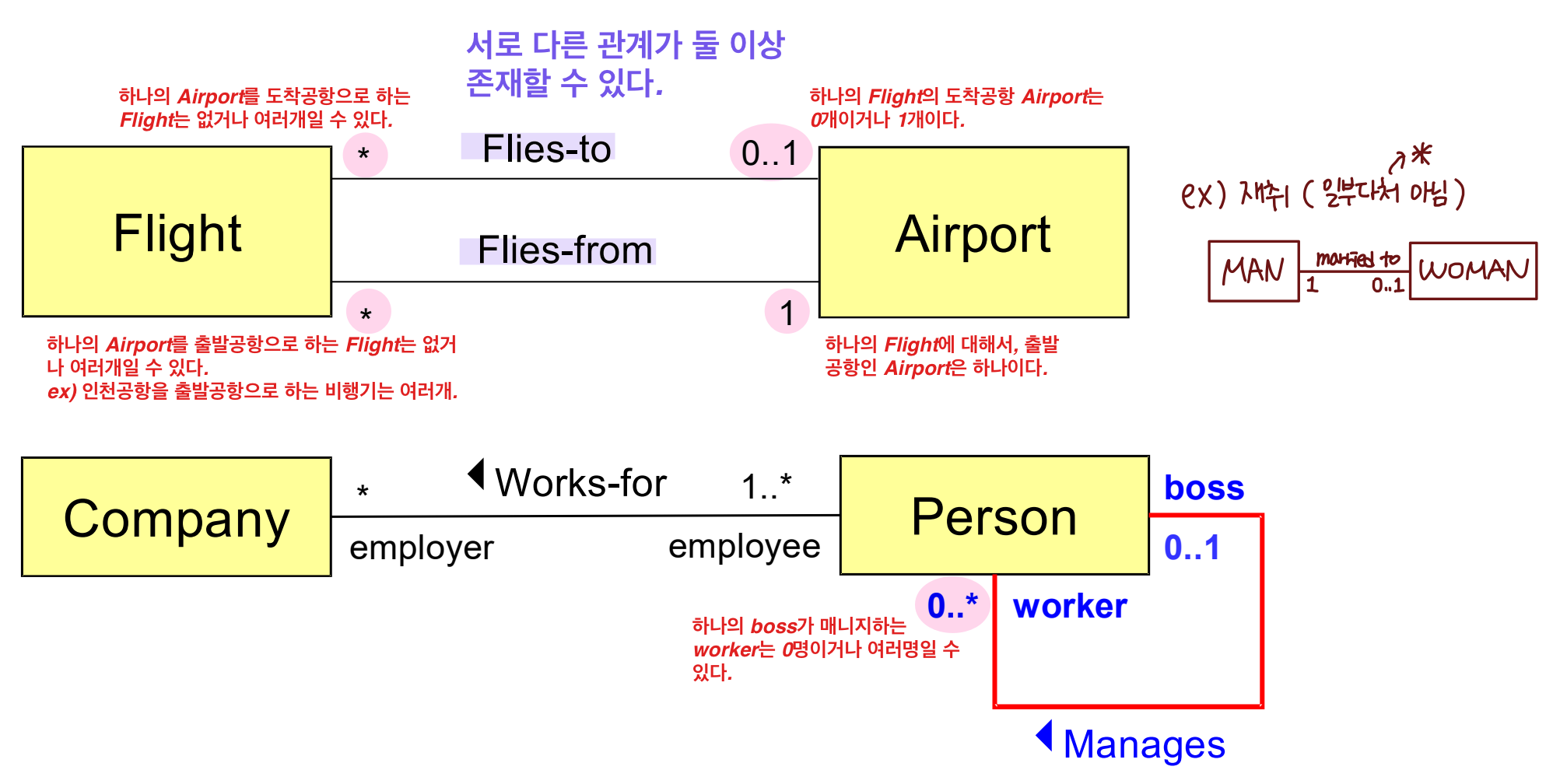
Unidirectional Association
A → B : A 는 상대방(B)를 볼 수 있고(visibility), 메시지를 보낼 수 있다.
Association Naming Convention
- TypeName - {VerbPhrase} - TypeName
- verb phrase 는 '-' 로 구성한다.
Useful Associations
⭐️"Need-to-know" associations
- 요구사항을 충족하기 위해 기억해야 하는 관계.
"Comprehension-only" associations
- 문제 영역의 중요한 개념 클래스를 이해하는 데 도움이 되는 관계
Common Associations List
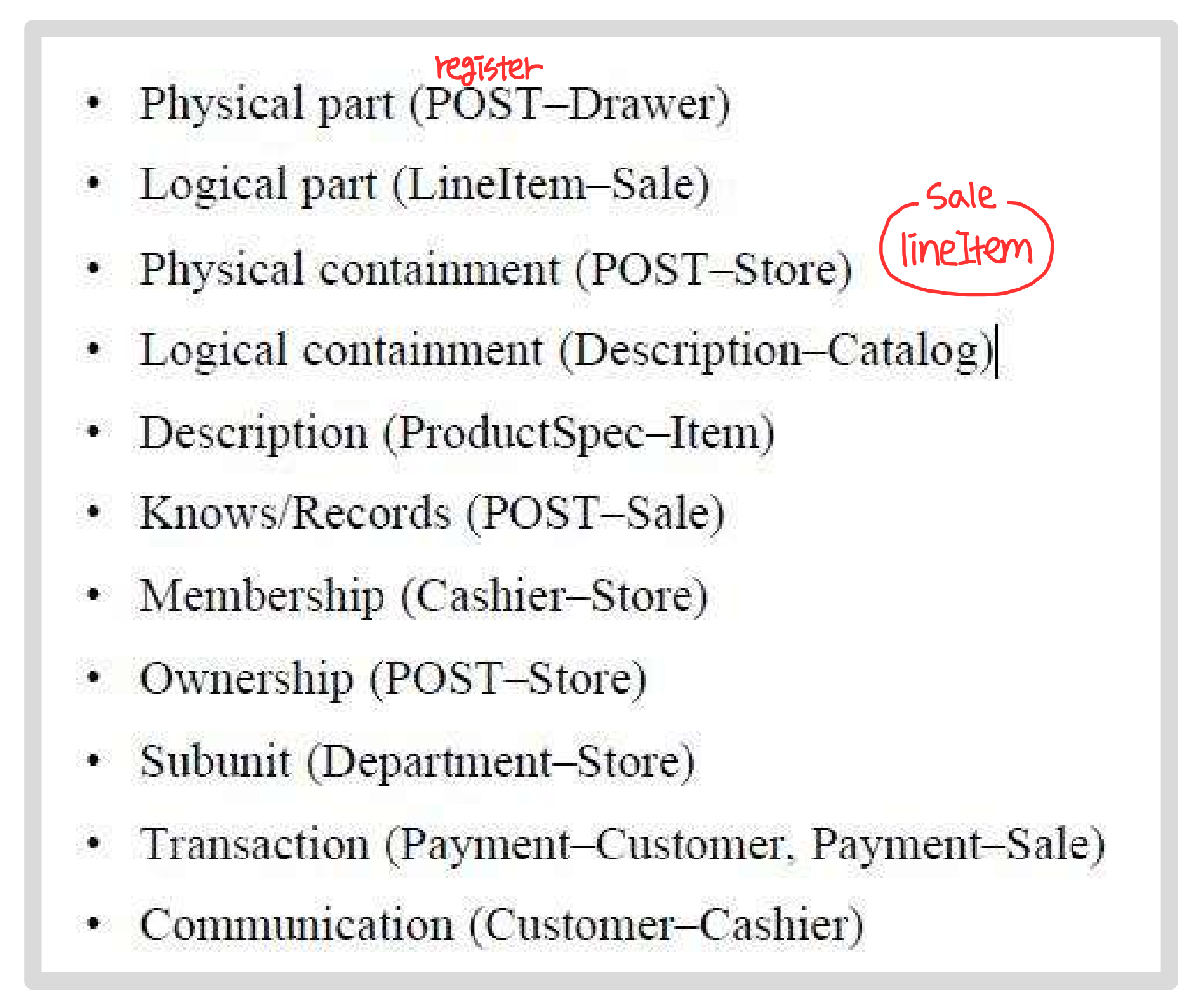
High Priority Associations
: priority 가 높을수록 "need-to-know" association 이 될 확률이 높다.
- A is a physical or logical part of B.
- ex) 사람 몸의 장기
- A is a physically or logically contained of B.
- ex) 서랍 속 물건
- A is recorded in B.
📌Attributes
: object 의 logical data value
- attribute 는 pure data value(simple atribute) 이다.
(pure data value 는 identity 를 가지지 않는다.) - struct, operation 을 가지는 것이라도 identity 가 없다면 → attribute
- attribute 로 표현함으로서 주위 관계를 더 잘 파악할 수 있다. (깔끔)
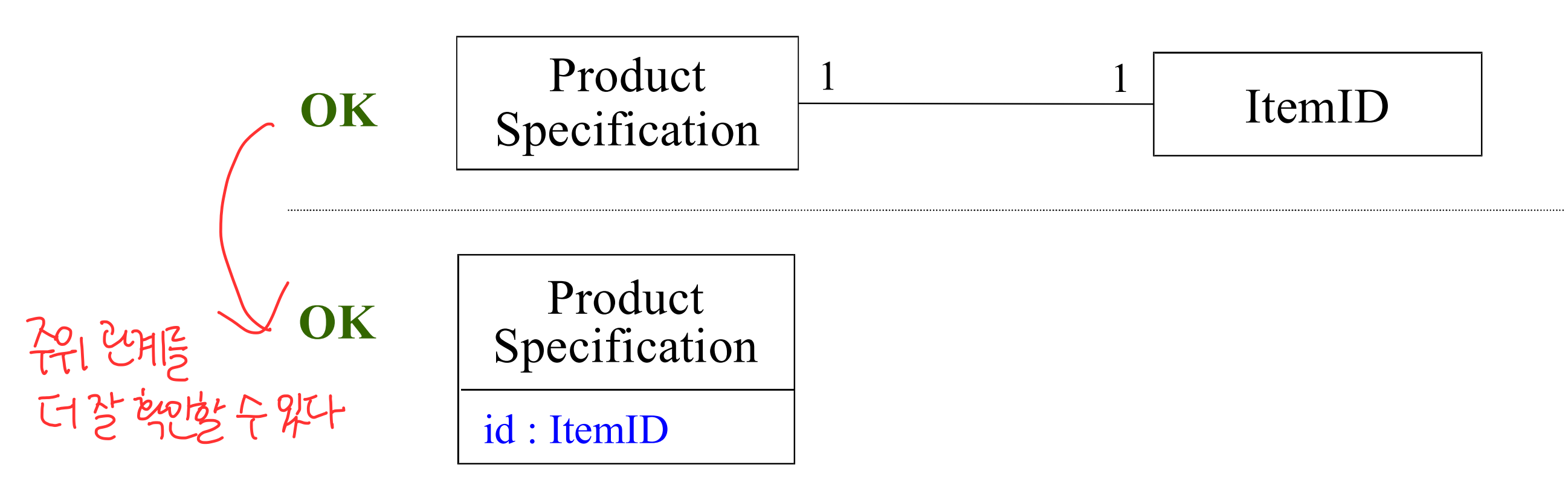
| object | attribute |
|---|---|
| identity O | identity X |
| mutable | emutable |
Common Simple Attributes
common simple attribute types (primitive data types)
: Boolean, Date, Number, String(text), TimeOther simple types (non-primitive data types)
: Address, Color, Phone Number, ...- struct, operation 을 가지더라도
- 이것이 다른 attribute 를 가지더라도
- 이것을 표현하는 unit 이 있더라도
- abstraction(concept)을 표현할 때도
→ 이는 identity 가 없다면 무조건 non-primitive type attribute 이다.
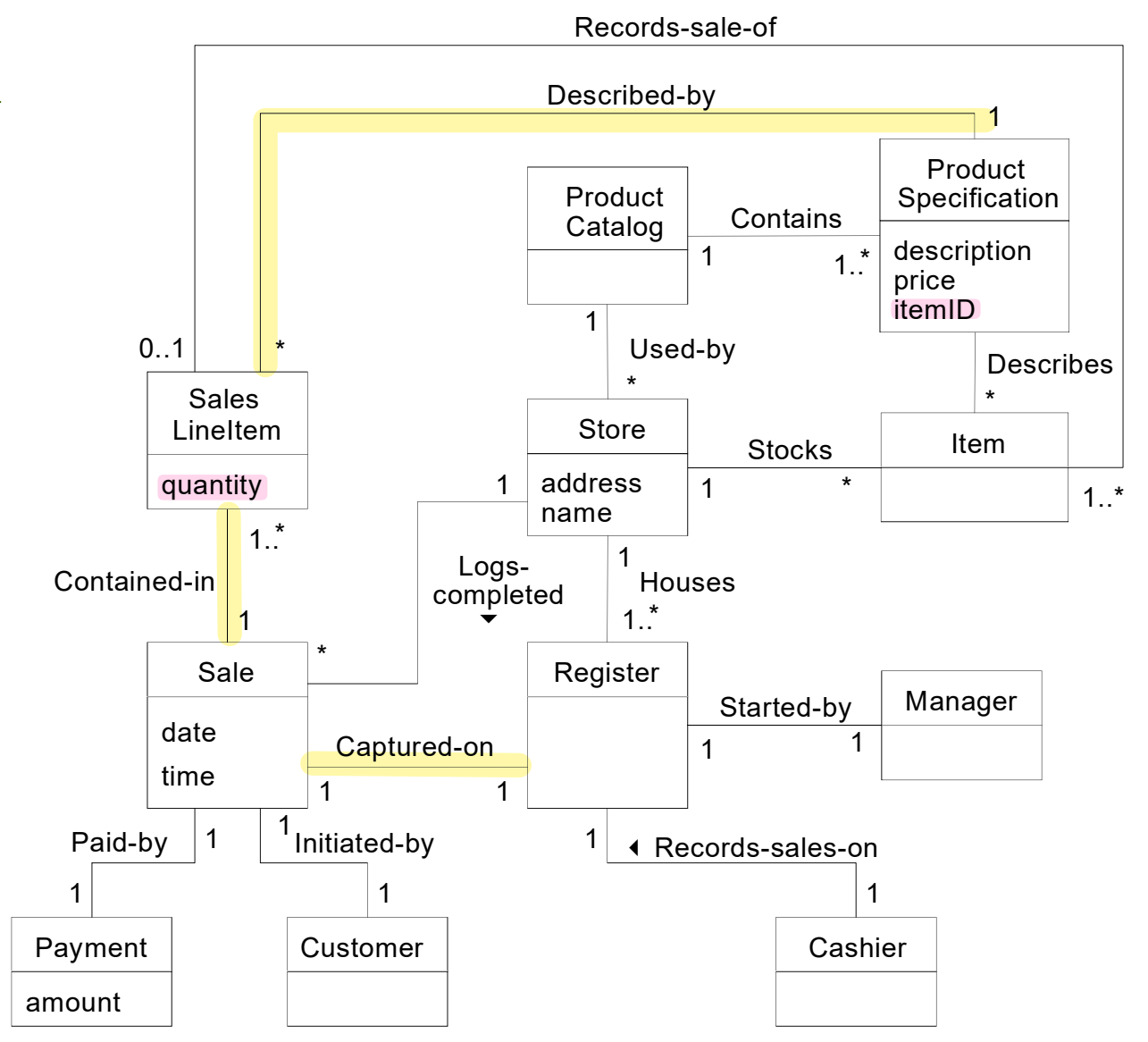
🌟Example : NextGen Model
Candidate Conceptual Class + Attribute
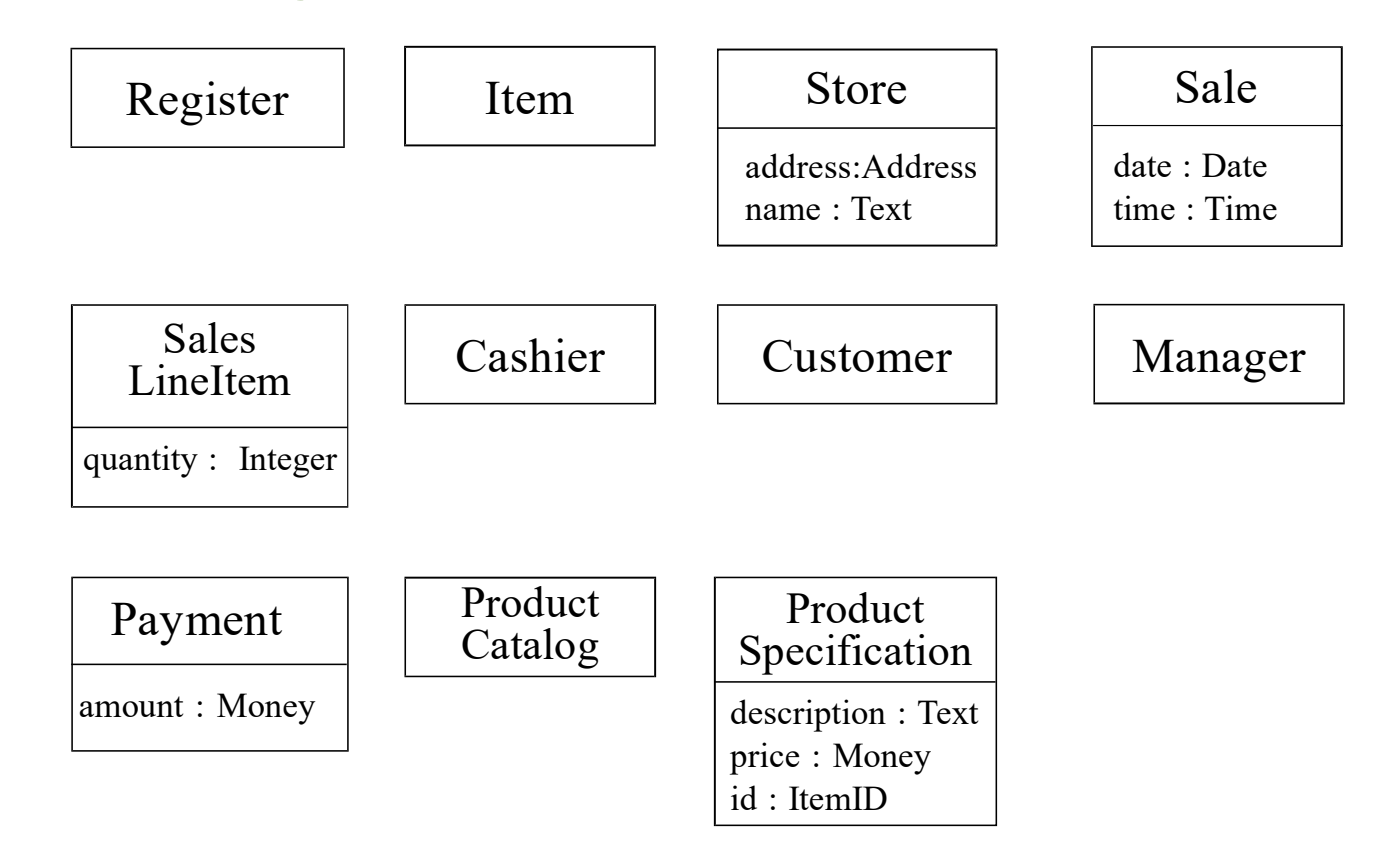
Domain Model
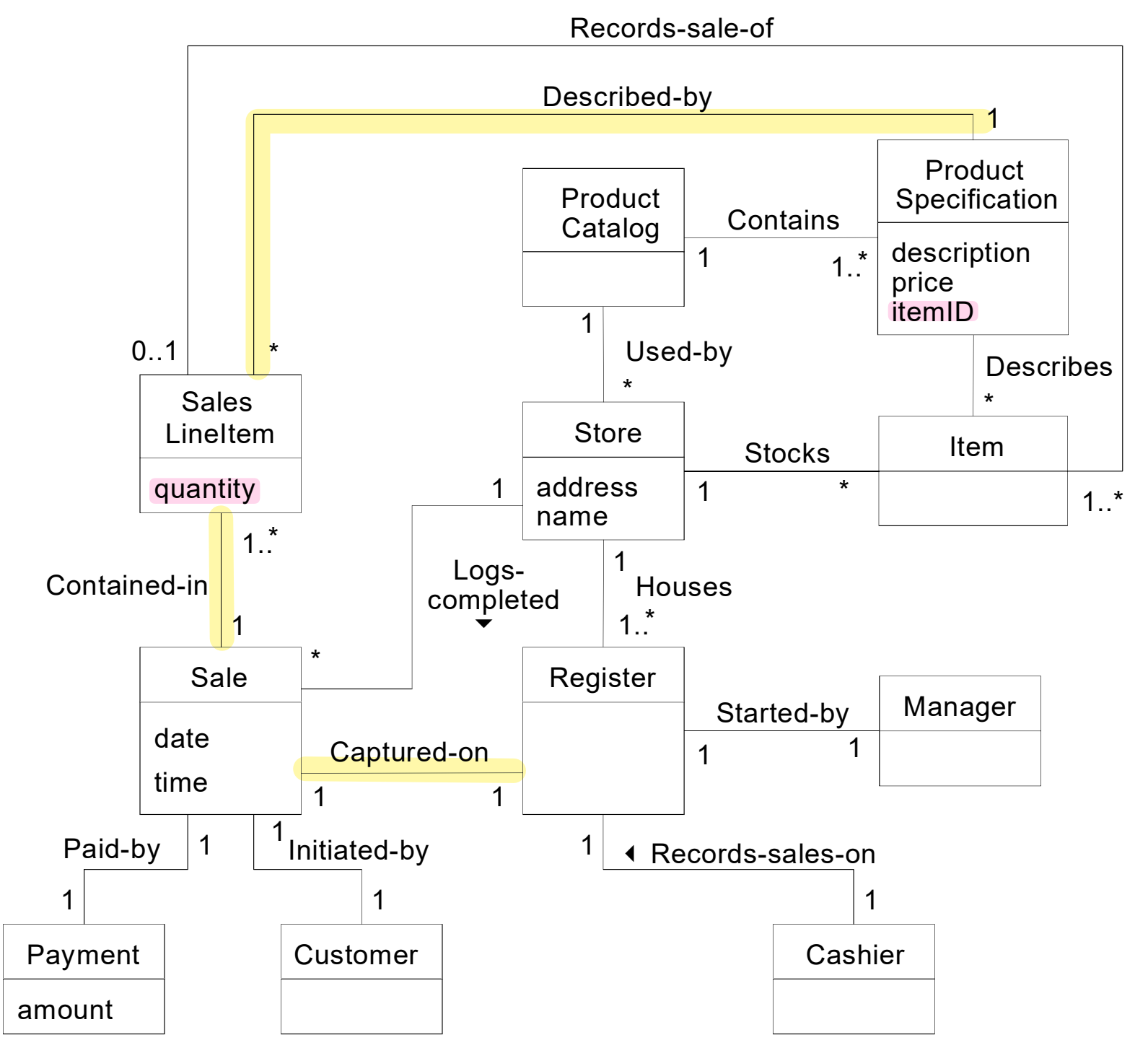
Contract
: provider, client 를 묶는 explicit(명시적) agreement(합의)
= {pre} + operation + {post}
- pre-condition : client 의 서비스 사용을 한정한다.
- post-condition : operation 의 실행으로 나오는 결과를 보장한다.
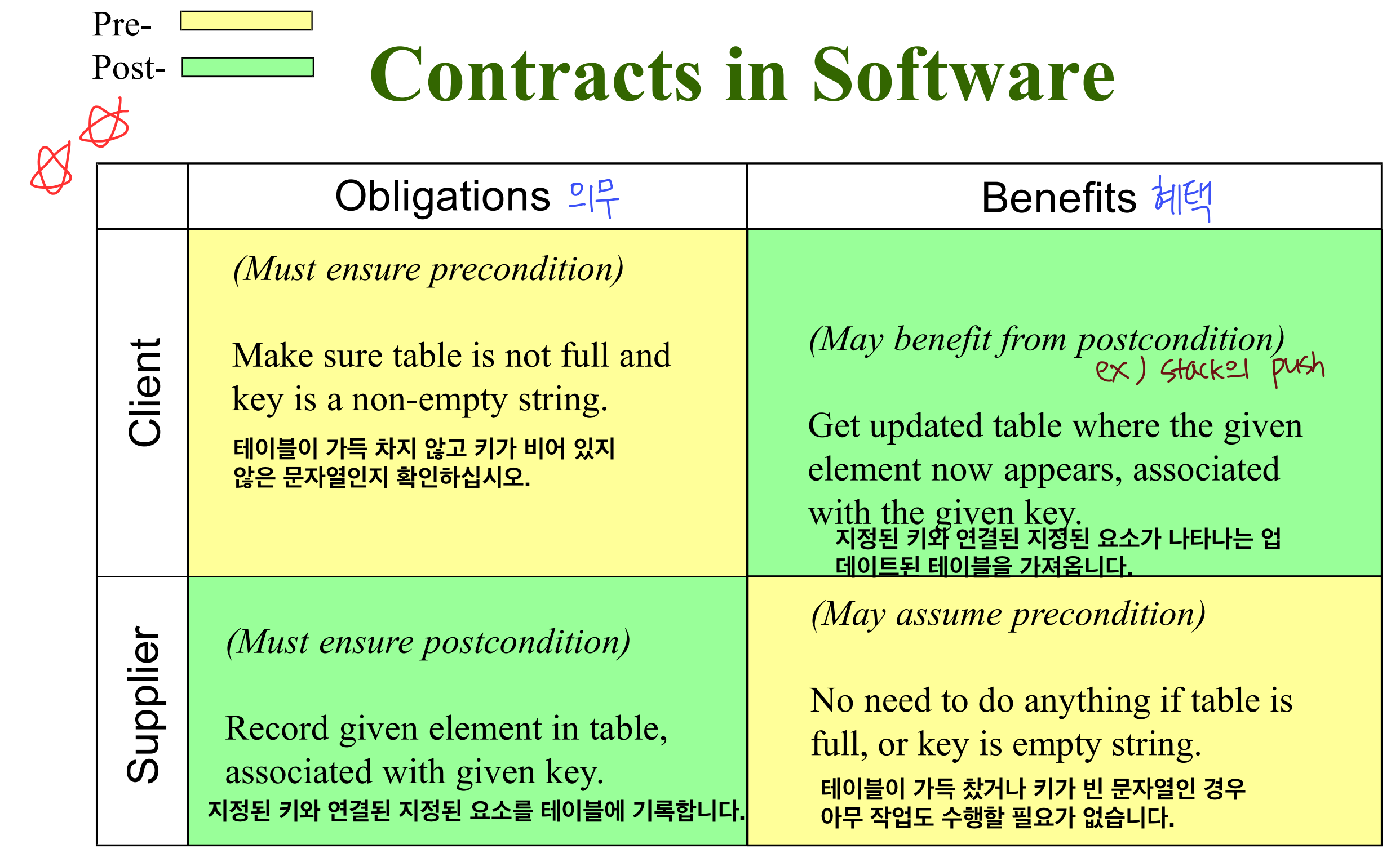
Client 가 의무(obligation), pre-condtion 으로 가지는 것을, Supplier 는 혜택(Benefit), post-condition 으로 가진다.
Supplier 가 혜택(obligation), pre-condition 으로 가지는 것을, Client 는 의무(obligation), post-condition 으로 가진다.
→ ⭐️당연함. Supplier 는 client 에게 어떤 행위를 하고, 만족시켜야 함. 즉 post-condition 을 의무로 지녀야함!!!⭐️ *
→ 반면에, client 는 의무(pre-condition)만 다 하면 혜택(post-condition)을 받을 수 있다.system operation 이 실행되고 나서의 system behavior 에 대해 기술한다.
operation 을 위해 contract 를 작성할 수 있다.
➡ operation 이 복잡하거나, core function 이라 생각되면 contract 를 만들자~.
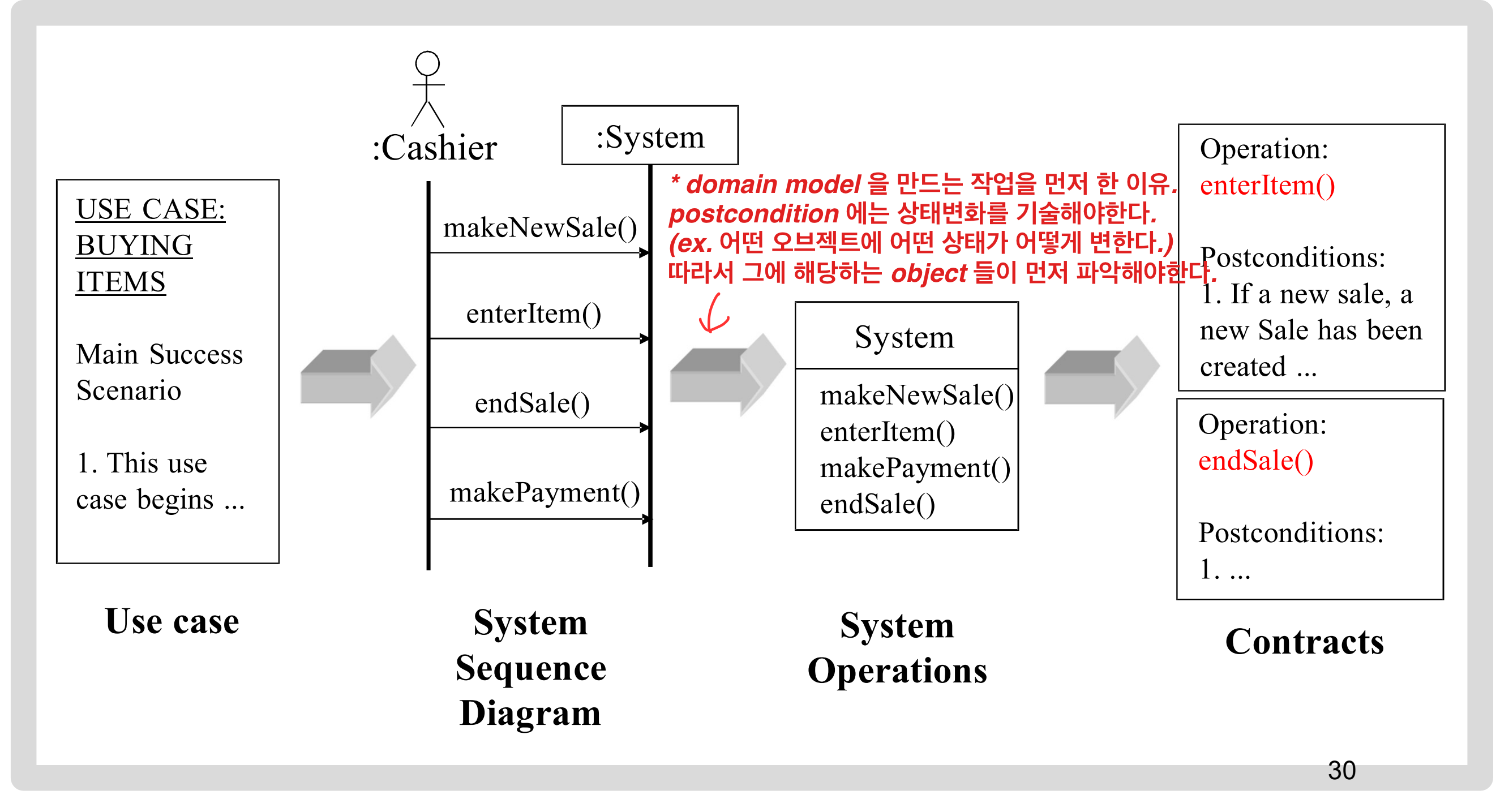
How to Make A Contract
- system sequence diagram 에서 system operation 을 식별한다.
- complex 하고, use case 에 대해 모호한 system operation 에 대해서 contract 를 만든다.
- 다음을 사용해 post-condition 을 설명한다.
- Instance 생성, 삭제
- Attribute 수정
- Association 생성, 파괴
과정 : Use case - SSD - System Operation - Contracts
🌟Example
Example1 : makeNewSale

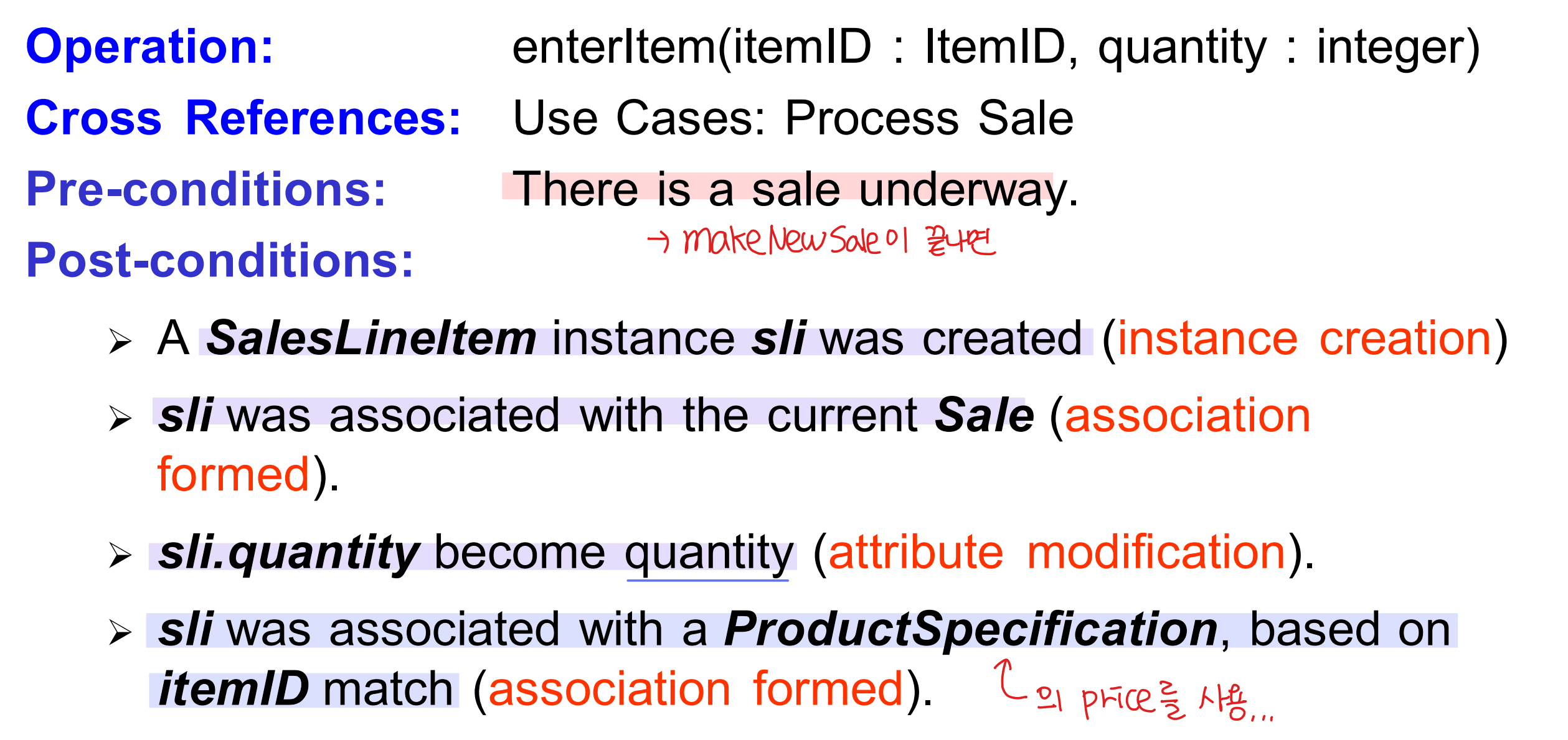
Example2 : enterItem
'* CS > 객체지향개발론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [객체지향개발론] 08 Grasp Patterns(1) | 09 Grasp Patterns(2) and Advanced concepts (0) | 2023.08.14 |
|---|---|
| [객체지향개발론] 07 Sequence Diagram (0) | 2023.08.08 |
| [객체지향개발론] 05 SSD and Domain Model(1) (0) | 2023.08.05 |
| [객체지향개발론] 04 Use Case (0) | 2023.08.04 |
| [객체지향개발론] UML (0) | 2023.08.02 |