[컴퓨터그래픽스] 01 Graphics System
(velog에서 옮겨옴 https://velog.io/@led156/%EC%BB%B4%ED%93%A8%ED%84%B0%EA%B7%B8%EB%9E%98%ED%94%BD%EC%8A%A4-Graphics-System)
Graphics System
Raster image vs Vector image
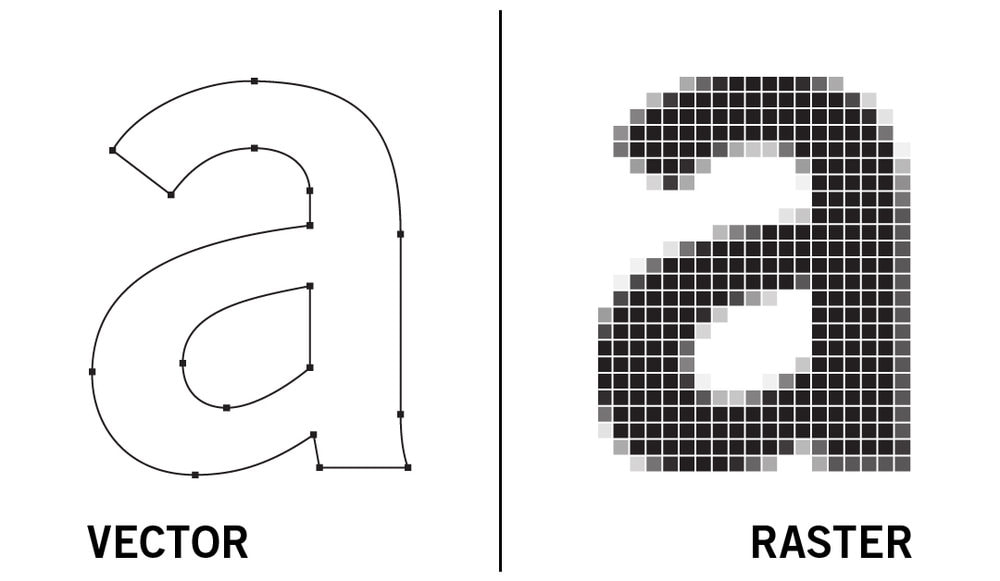
Raster image
: a rectangular array of pixel
- Drawing
- outline primitives : 외부 line을 점으로 표현
- filled primitives : 그 안을 채울지 결정
Vector image
: a array of dot
- Drawing : 약간 한붓 그리기
Graphic System (device)
Raster Devices
- Output
- Display
- LCD(Liquid Crystal Display) : Transmissive(투과성)
- LED(Light-Emitting diode Display) : Emissive(방출성)
- Hardcopy
- ink-jet printer : Binary
- dye sublimation printer : Continuous tone
- Display
- Input
- 2D array sensor
- digital camera
- 1D array sensor
- flatbed scanner
- 2D array sensor
Raster-scan display
- 물체를 각 스캔 라인에 걸쳐 이산 포인트의 집합으로 나타낸다.
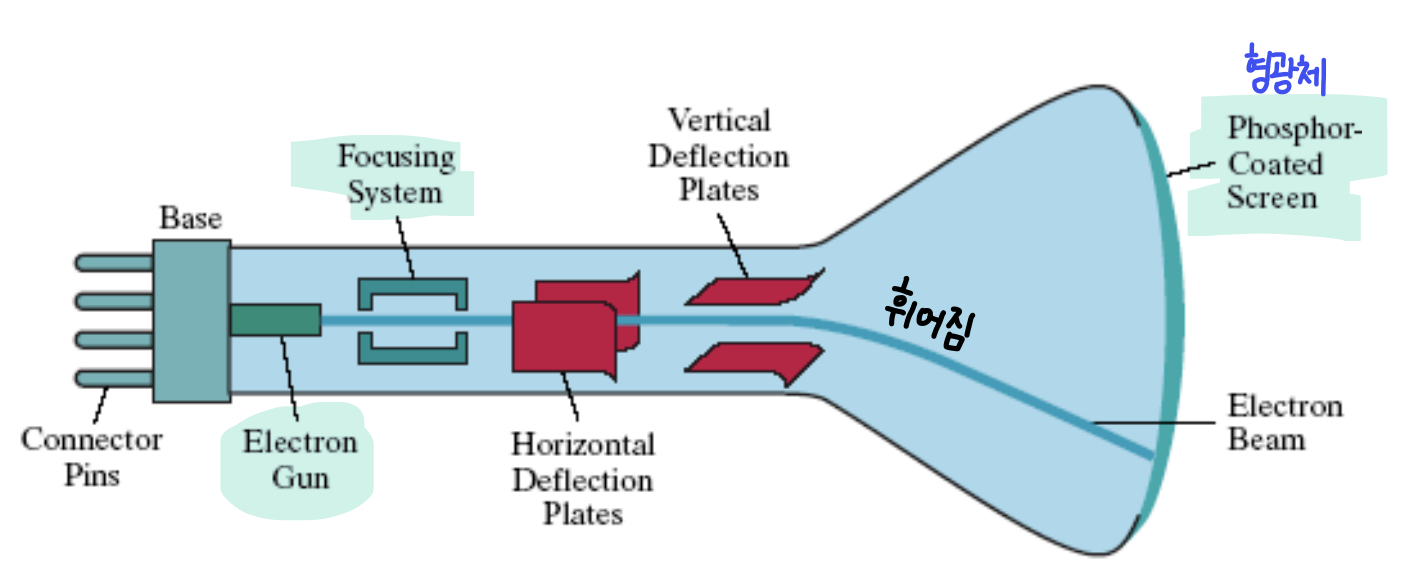
CRT (Cathode-Ray Tube)
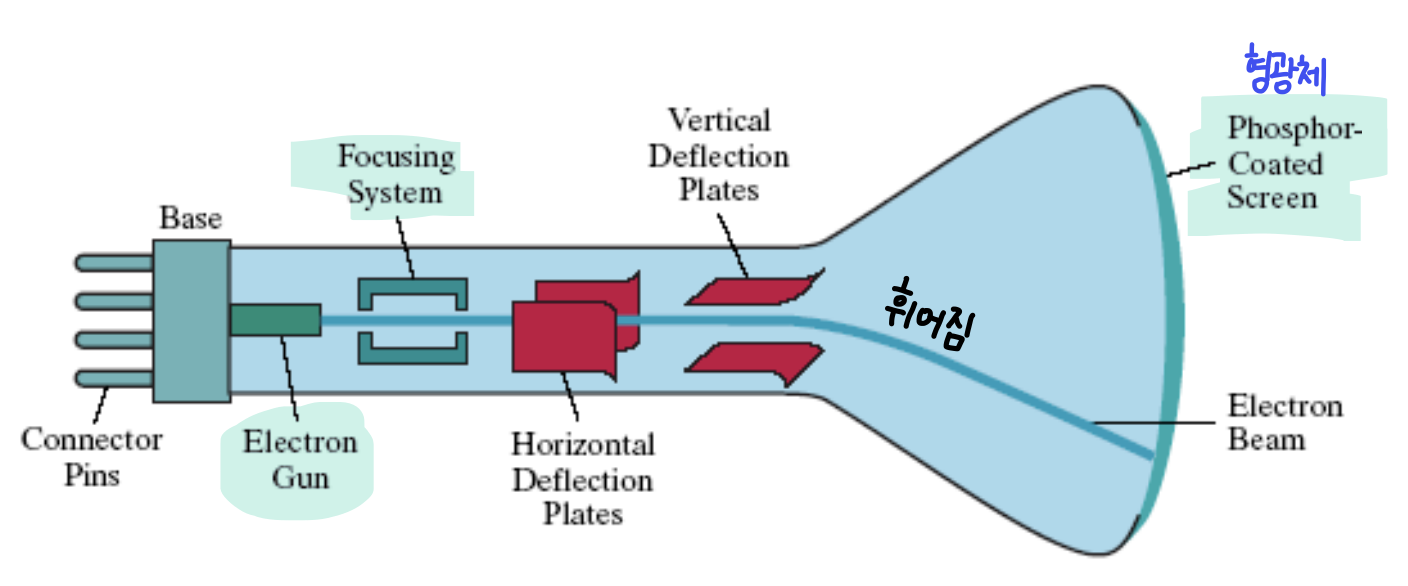
- Electron gun 이 electrons 를 cathode(음극)에서 방출(emit)한다.
- Anode(양극)은 electrons 를 가속시키고, 끌어당긴다.
- electrons 는 focusing and deflection systems 를 통과(pass)한다.
- electrons 는 phosphor-coated screen 에 부딪(hit)힌다.
- phosphor 에 의해 빛이 방출된다.
Vector CRT (random-scan) :
- beam 을 조종(steering)하는 전압은 일정한 속도로 변함.
Refresh CRT :
beam 에 의해 phosphor 가 짧은 시간동안 빛을 방출.
⇒ CRT가 리프레쉬함으로써 같은 경로를 역추적한다. (eg. 60Hz)
Noninterlaced(한꺼번에 리프레쉬) vs. interlaced display(프레임별로 짝수, 홀수 라인을 리프레쉬)
Color CRT
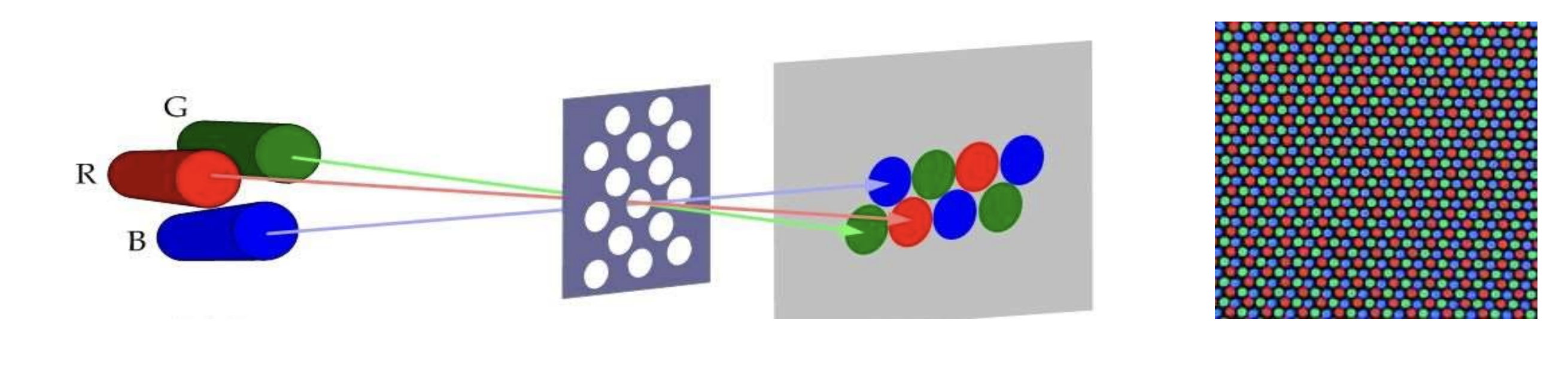
- 작은 그룹안에 세 가지 RGB phosphors 가 존재.
- shadow-mask (작은 구멍이 있는 금속판) 을 사용하여 적절한 색만 excite(들뜨다)하게 함.
- 세 가지 빔의 강도를 변화시켜 색 구현.
Flat-panel display devices (raster based)
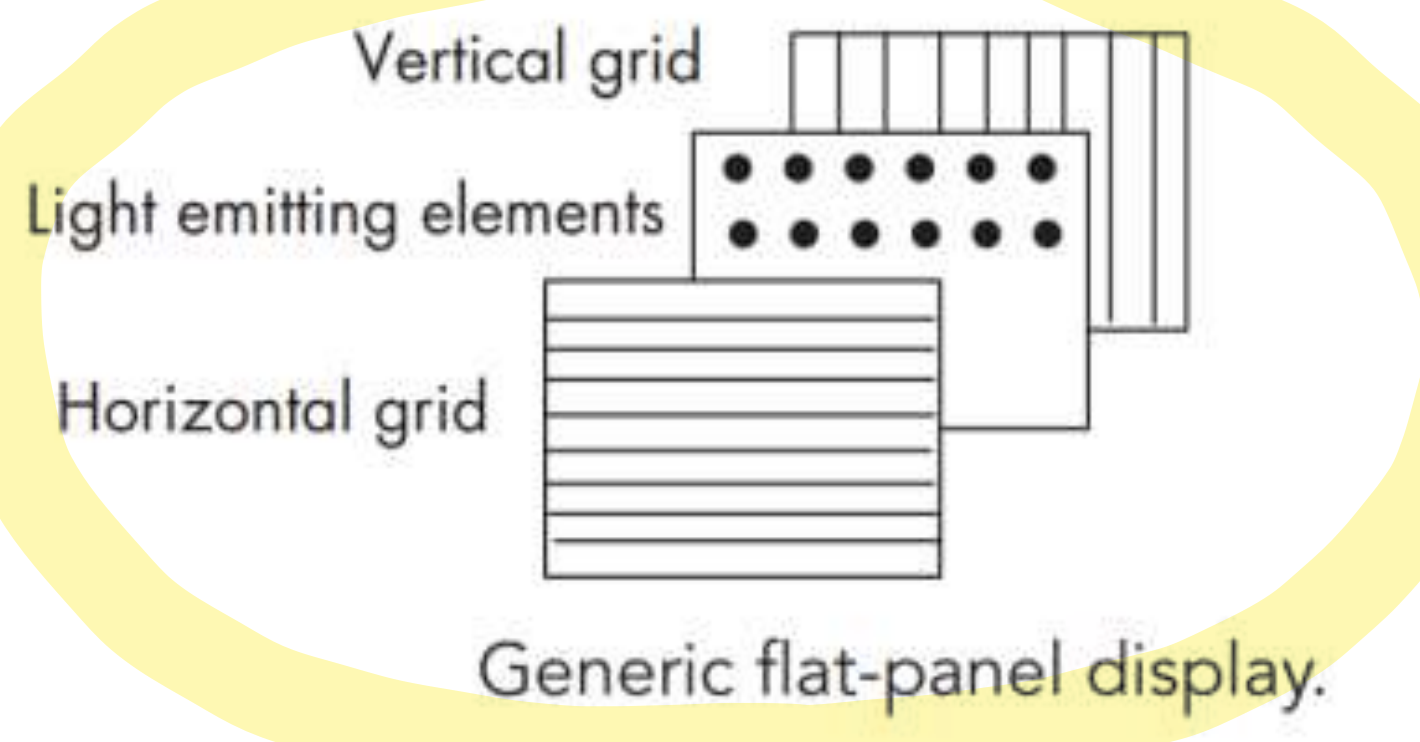
- two-dimensional grid 를 사용해, 개별 light-emitting elements 를 처리한다.
- gird 사이즈에 따라, resolution(해상도)가 고정된다.
PDP (plasma Display Panel)
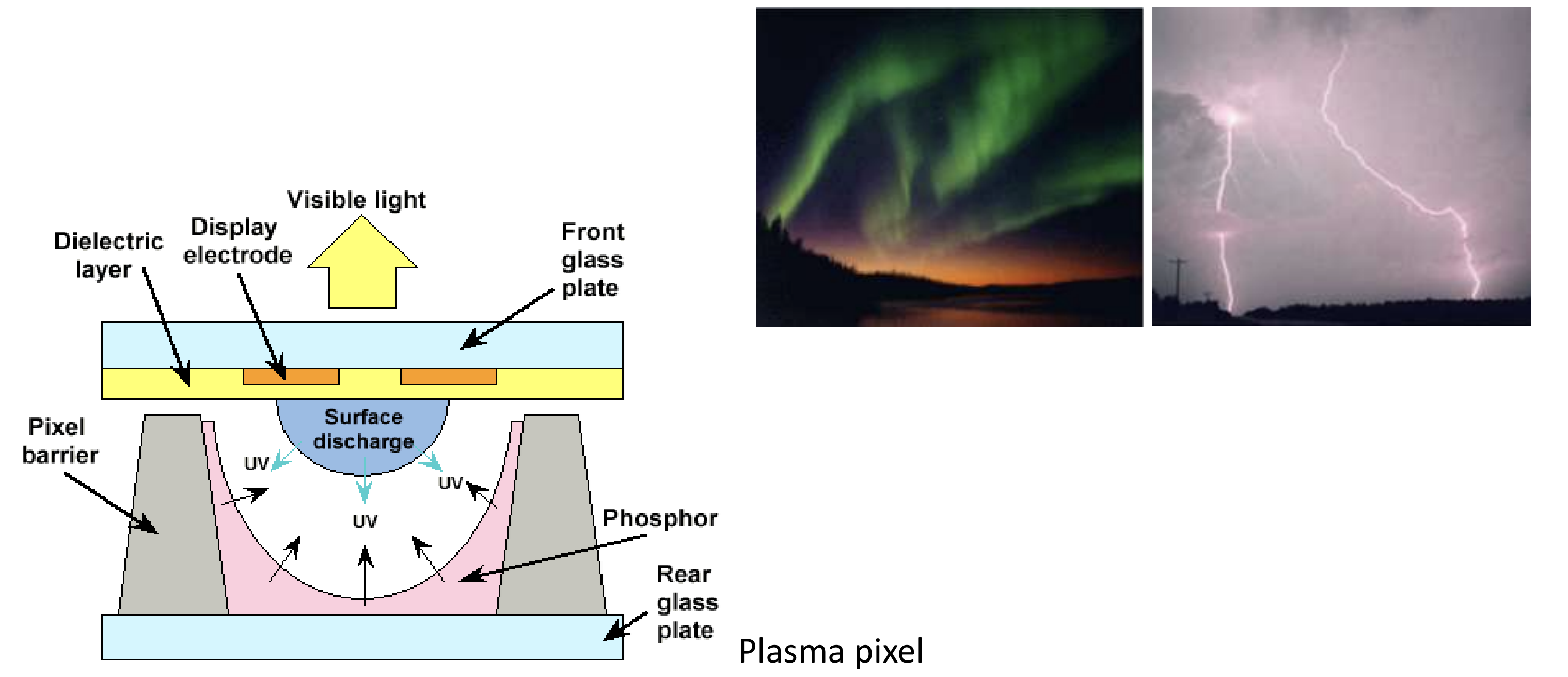
- glass panels 사이에 embedded(내장된) 한 energize gases 에, grid 의 전압이 전력을 공급한다.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
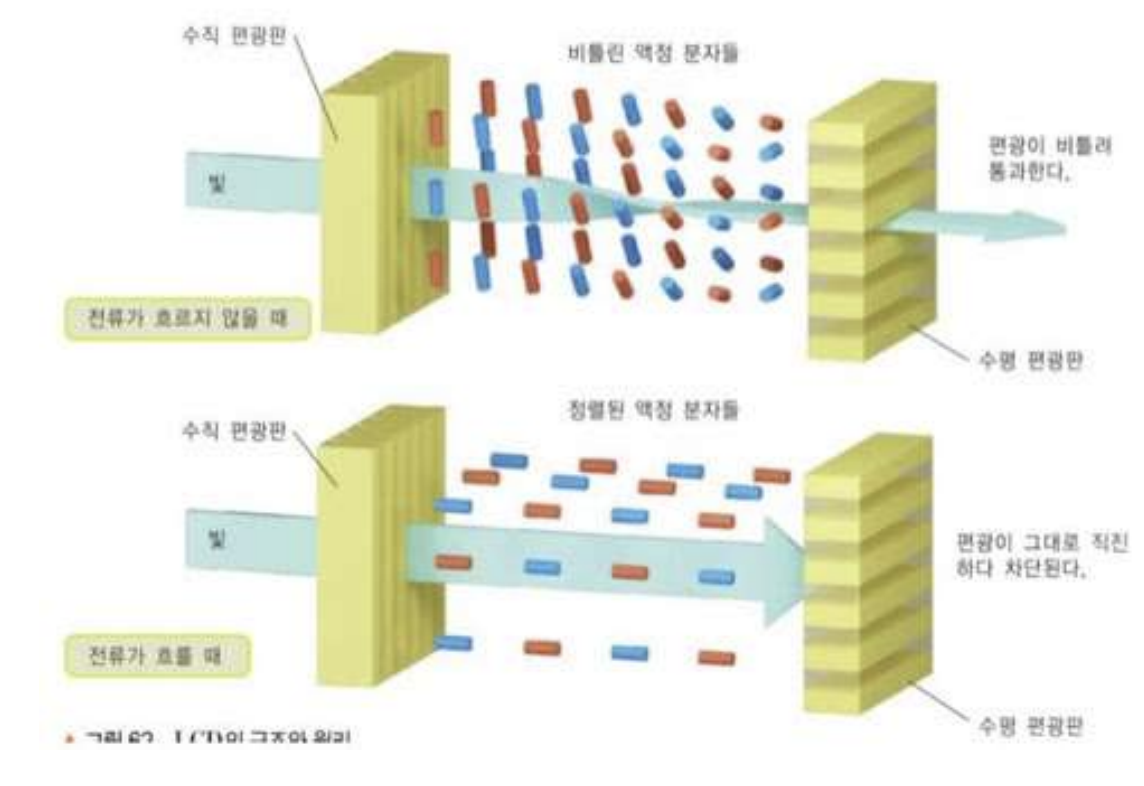
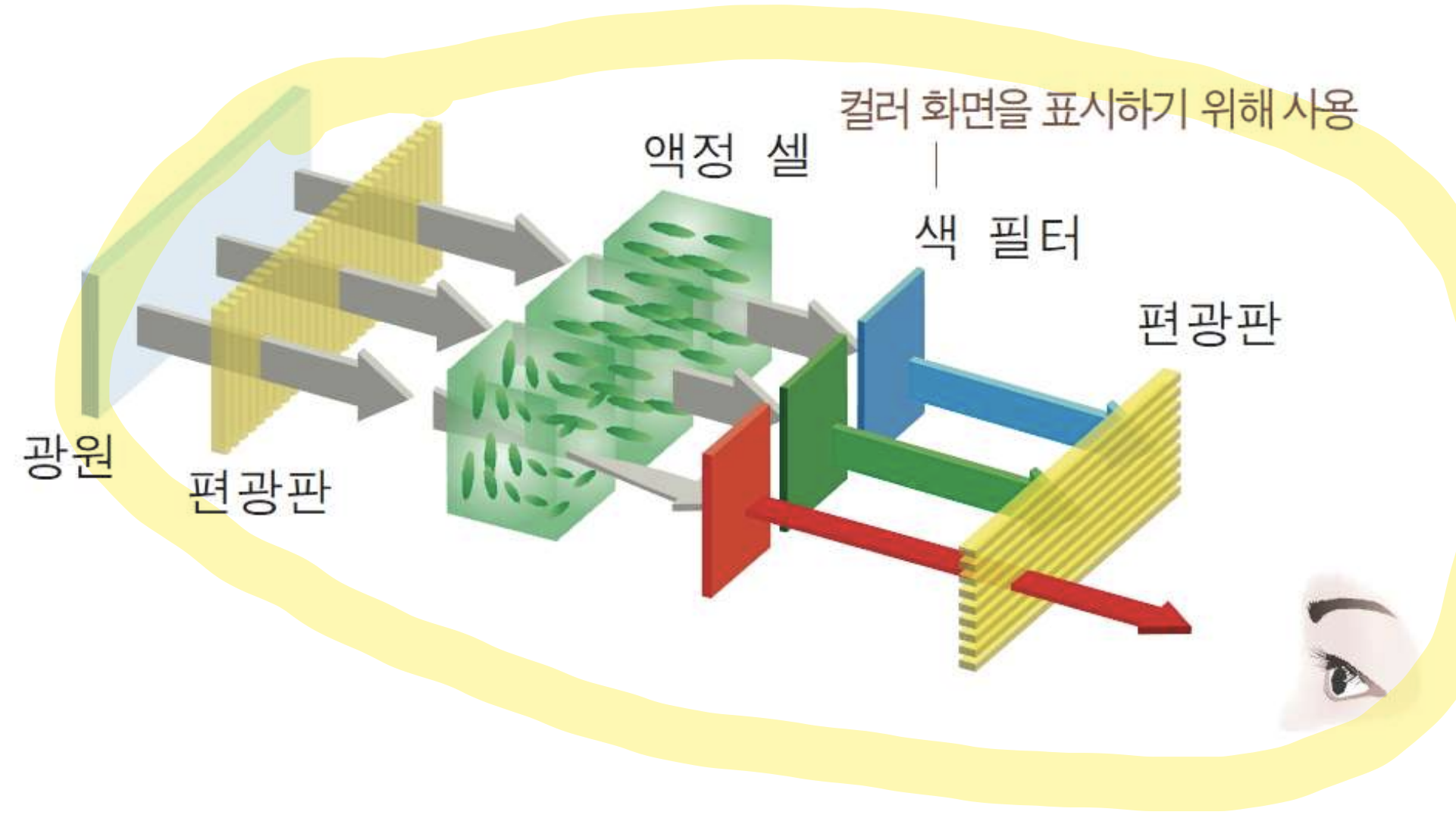
- Transmissive displays : 픽셀이 빛을 방출하지 않음. 다양한 양의 빛이 그들을 지나간다.
→ 광원 필요 (Backlight)LED (Light-Emitting diode Display)
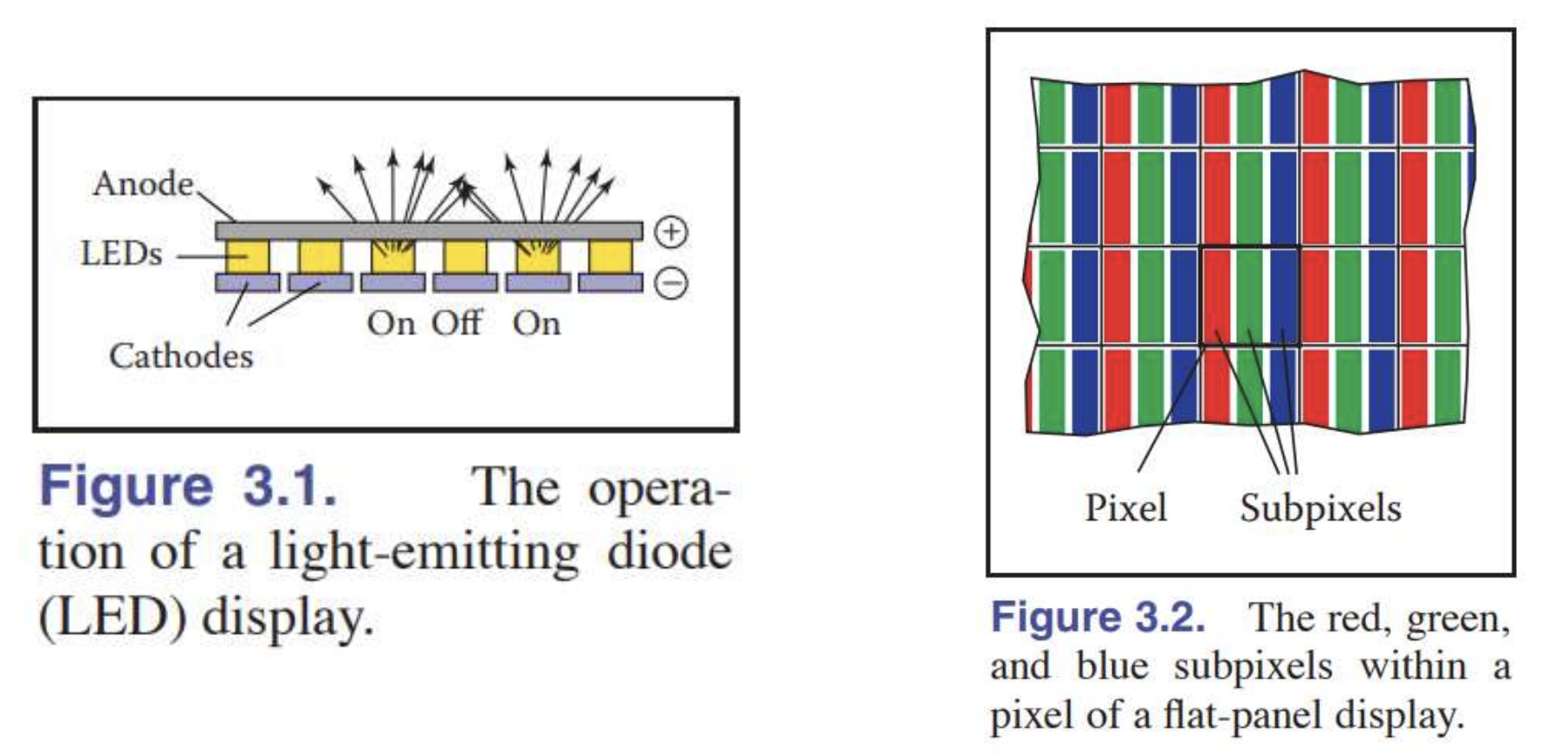
- 각 픽셀이 (semiconductor device인) LED 로 구성되어 있고, 그는 강도를 가진 빛을 방출한다.
Hardcopy Devices
- Halftoning : 망점. 크기나 간격에 따라 상을 따라 만드는 점.
- Digital Camera
- 2D array input device : image sensor 는 빛에 민감한 픽셀 그리드를 가진 semiconductor device 이다.
- 카메라 렌즈는 scene 을 센서에 투과한다.
- 픽셀 센서는 그에 떨어지는 빛 에너지를 측정한다.
- Demosacicking : 누락된 이미지 값을 채우는 소프트웨어 기법
- 픽셀 수에 따라 resolution(해상도)이 결정됨.
- 2D array input device : image sensor 는 빛에 민감한 픽셀 그리드를 가진 semiconductor device 이다.
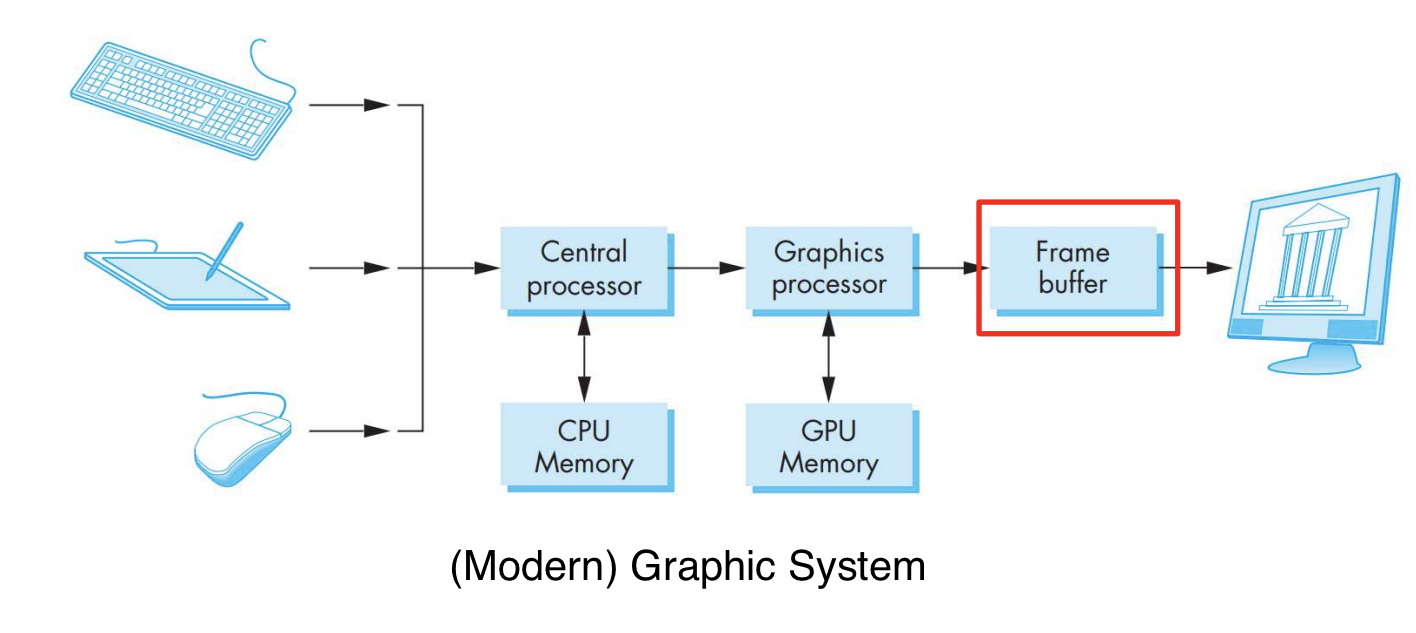
Graphics Archtecture
Early(초기) graphics system (based on vector graphics) - cpu 가 다 담당.
- 애플리케이션을 실행하여, line segments 의 end points 를 계산.
- CRT 디스플레이로 정보가 전송됨.
Display processors
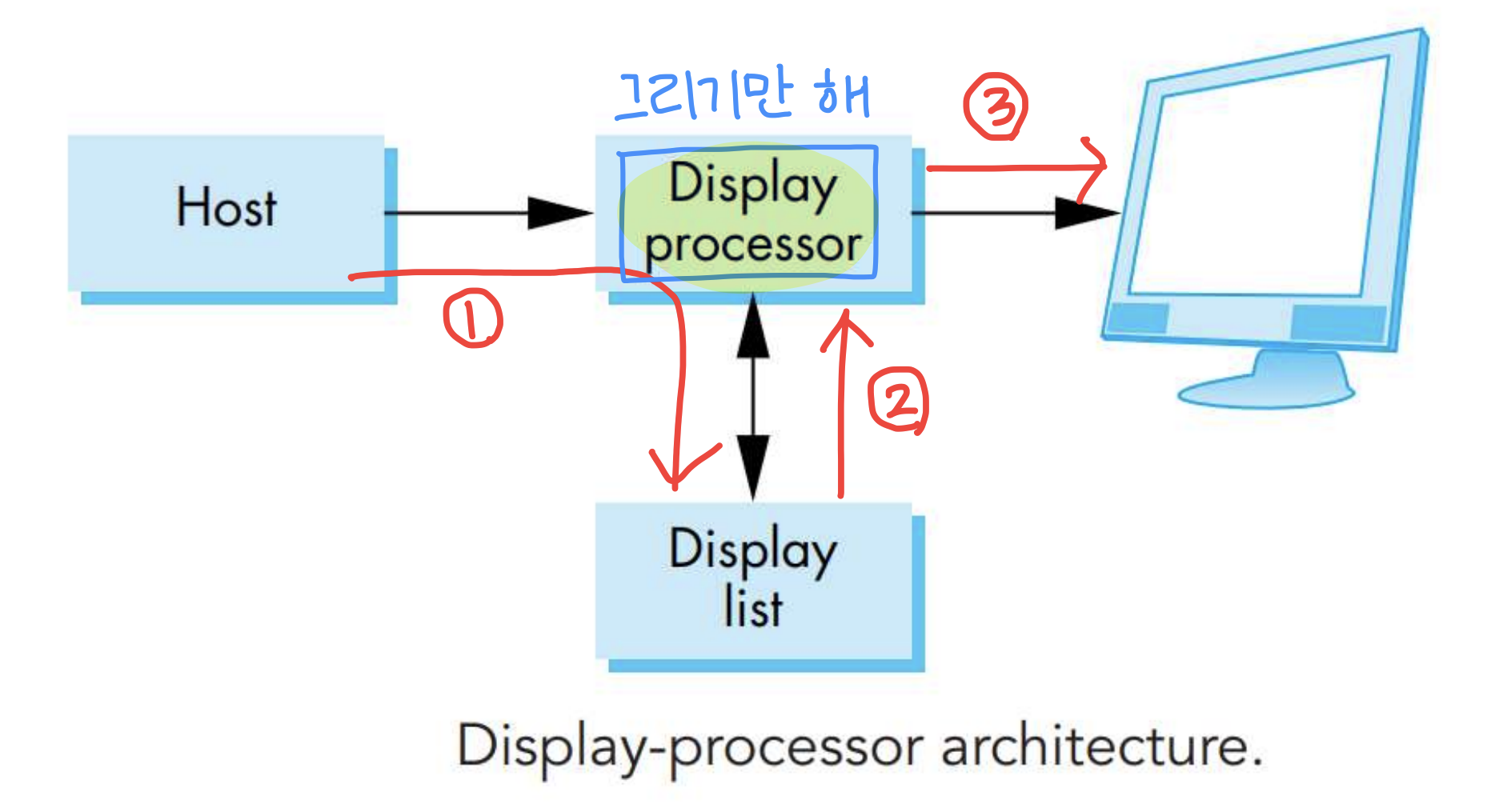
- 정보가 display processor 의 자체 메모리에 저장.
Pipeline Architecture
- throughtput(처리량), latency(대기시간) 로 시스템 평가.
- repetitive computations 에 효과적이다.
Graphics Pipeline
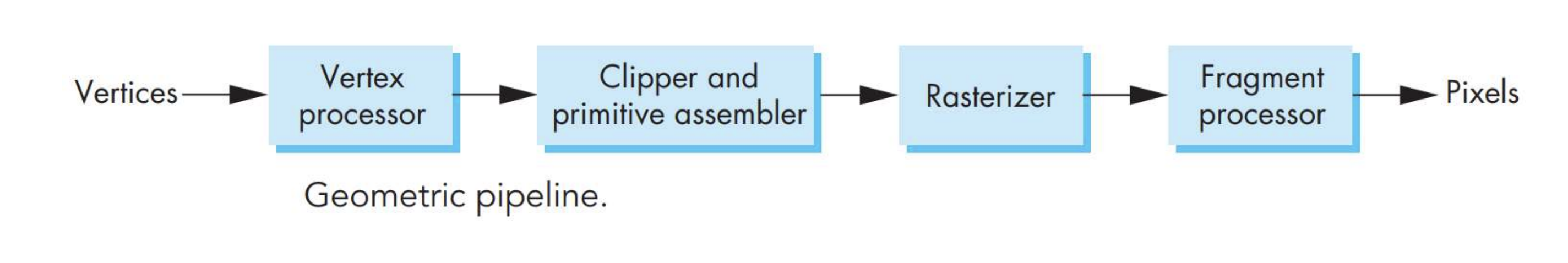
object(vertices) 집합을 frame buffer 의 픽셀로 처리한다.
Vertex processor
- 각 vertex 를 독립적(independently)으로 처리한다.
- Tasks: coordinate transformations, color computations of each vertex
Clipper and privitive assembler
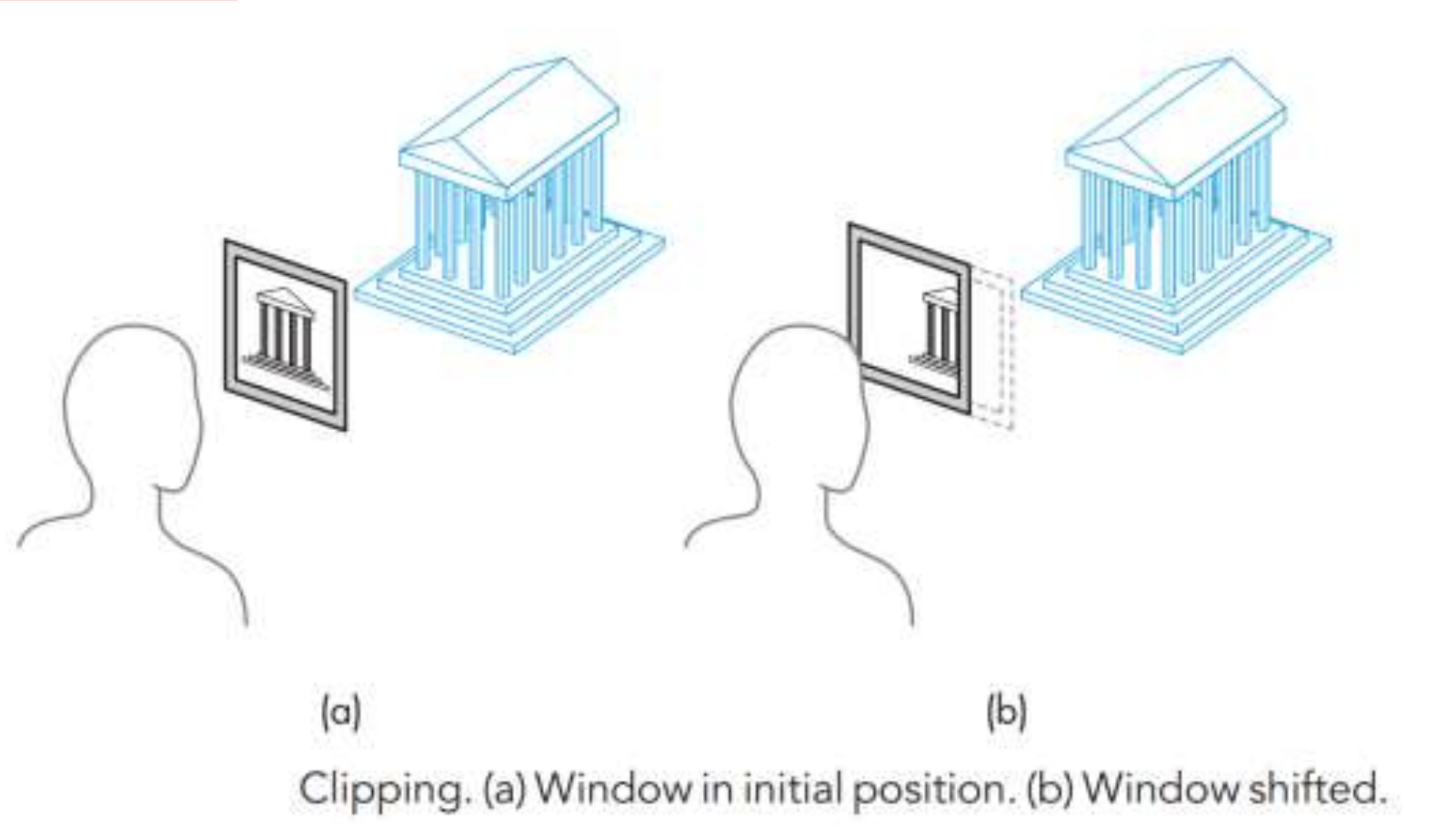
- camera view 에서 벗어난 장면의 일부를 Clip.
- primitive-by-primitive basis 에 근거해 Clipping 해야한다.
- Output: a set of primitives with projections appeared in the image(이미지에 투영되어 나타난 primitives 요소 집합.)
Rasterizer
- frame buffer 의 픽셀로 primitives 집합 변환.
- 각 픽셀의 픽셀 정보를 결정한다. (eg. computing blended colors in polygons)
- Output: a set of fragments for each primitive (pixel with color, location, depth, etc.)
Fragment processor
- frame buffer 의 fragments 에서 픽셀 업데이트.
- 일부 fragments 는 장면 뒤에 있어, 보이지 않을 수도 있음.
- 텍스쳐 적용 가능
Image
function 으로 이미지 추상화(abstract) 가능. $I(x, y): R \rightarrow V$
- $R$ : rectangular area, $V$ : set of possible pixels
raster image 의 Pixel : 이미지의 point samples
location of a pixel
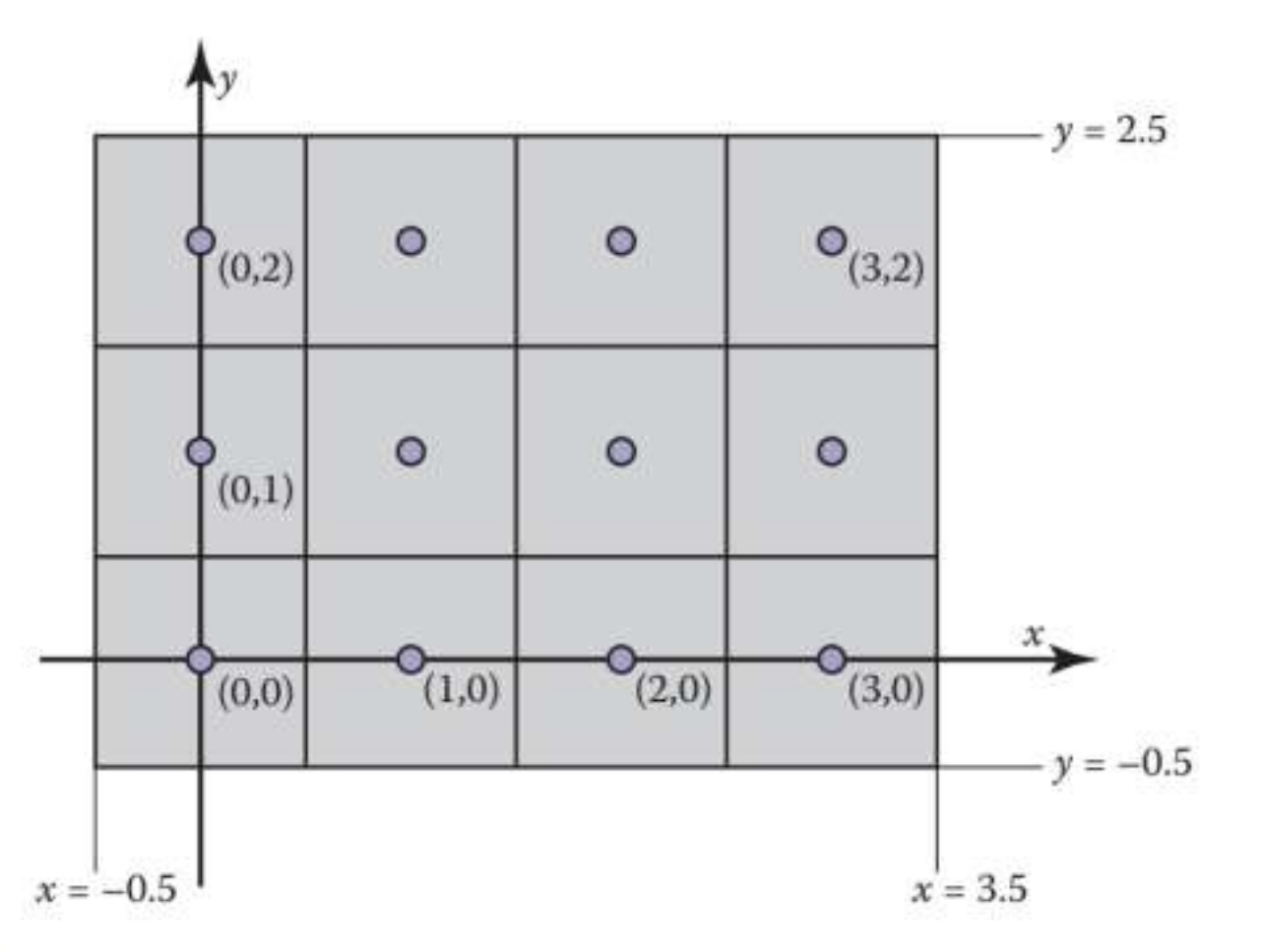
- pixel coordinates : $(0, 0), (n_x-1, n_y-1)$
- domain of pixel $(i, j)$ : $[i-0.5, i+0.5]\times [j-0.5, j+0.5]$
Pixel Values
해당 픽셀에서 RGB 빛을 나타내는 강도가 값으로 존재.
⇒ 이미지는 number values 의 array 이다.
강도 값은 minimum, maximul value 로 제한됨. (보통 [0, 1])

HDR(High Dynamic Range), SDR(Standard Dynamic Range)
Gamma
linearly mapping : 픽셀 값의 범위 - 빛의 강도 범위(0 : black, 1 : white, 0.5 : half-gray)
모니터는 입력값에 대해 nonlinear 함. (eg. 0.5 outputs 0.25)
Monitors are characterized (approximately) by 𝛾 value
: $\newline display,Intensity=(maximum ,intensity)a^\gamma\newline$
eg) $0.25 - 1\cdot (0.5)^\gamma,, \therefore \gamma = 2$
Gamma correction
: $a' = a^{1/r}$, (a: 모니터에서 실제로 얻은 값) $\newline$
eg) $a' = (0.25)^{1/2} = 0.5$
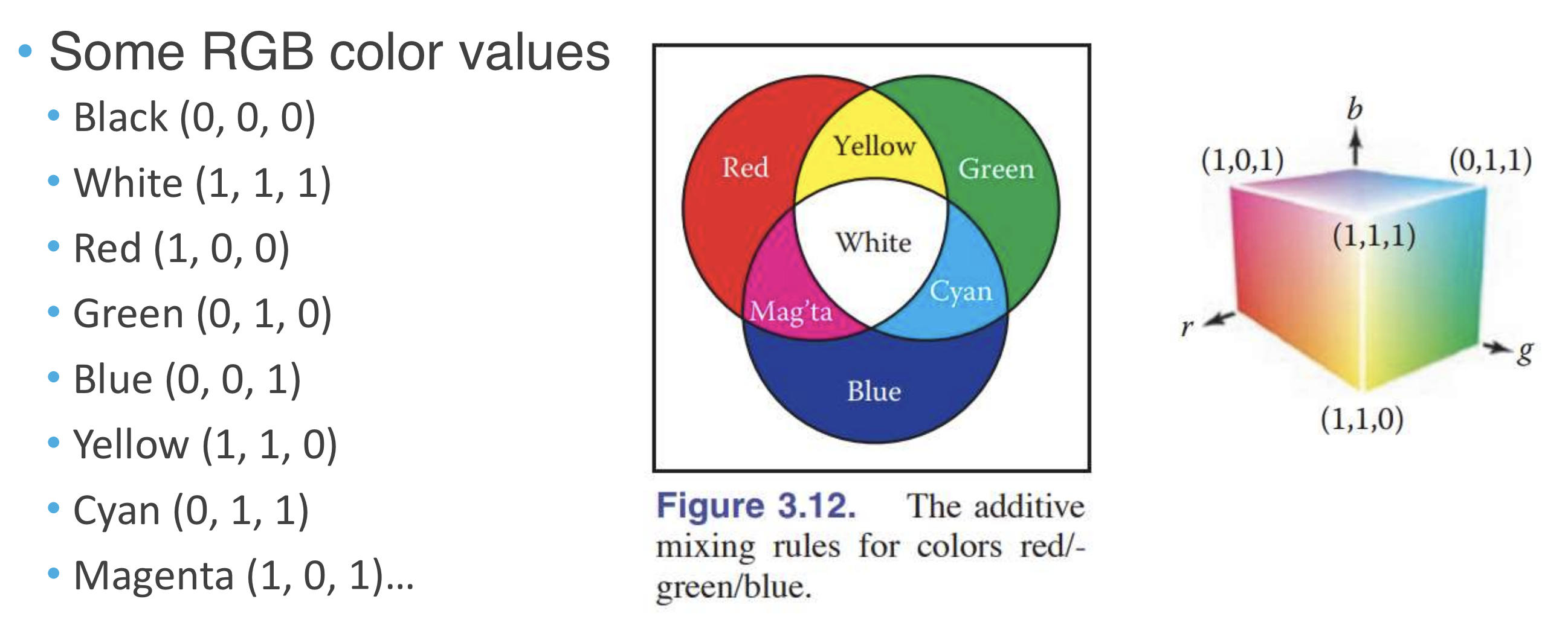
RGB Color
apply additive(가산) mixing rules
Alpha Composition
pixel 에 transparency information 추가.
→ foreground/background 합성(compositing)에 유용
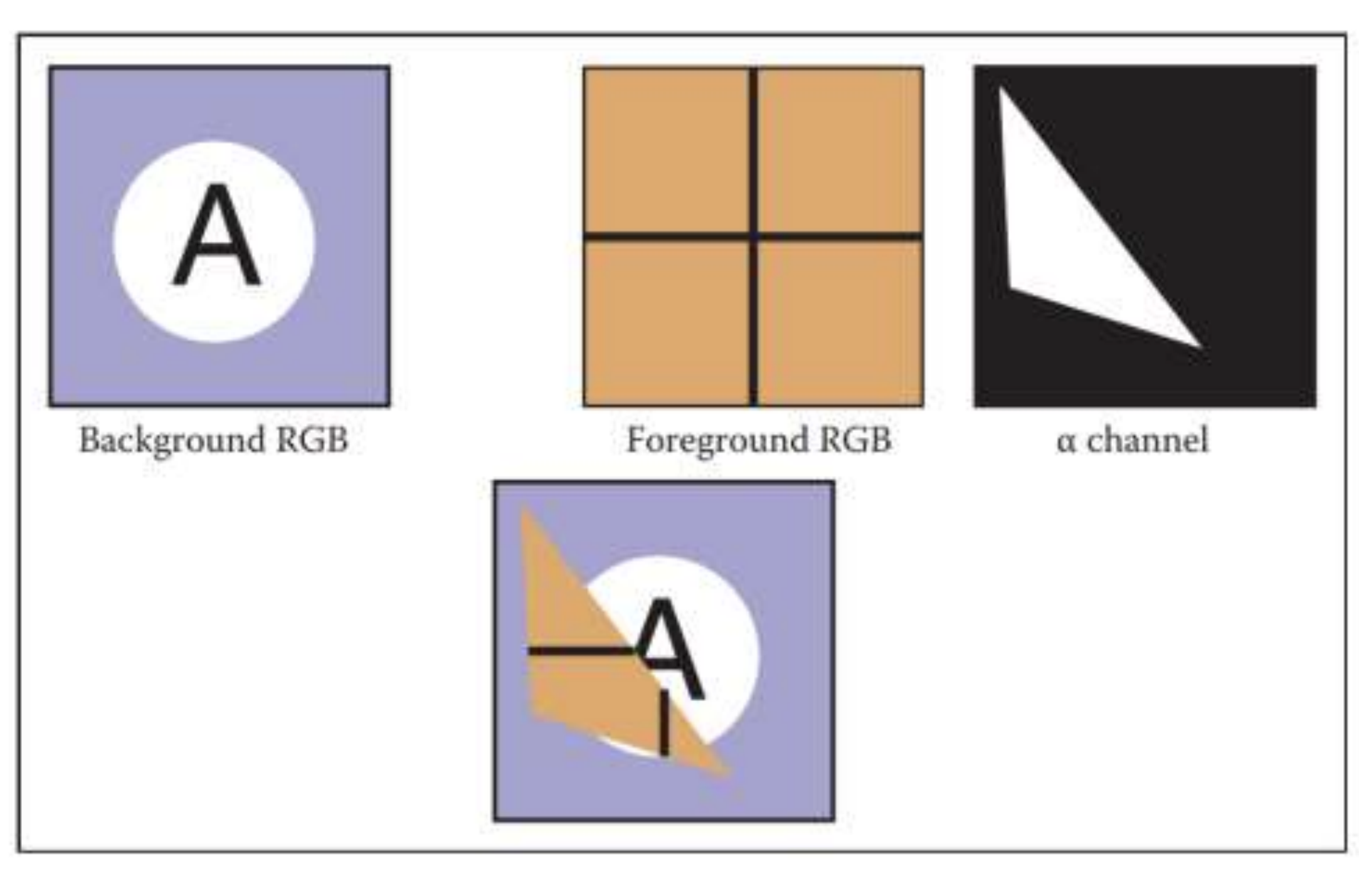
$\alpha$ : foreground layer 에 의해 가려지는 픽셀의 비율(fraction)
Color of a pixel : $c = \alpha c_f + (1-\alpha)c_b$
- $c_f, c_b$ : foreground and background color value
alpha channel 에 alpha value 가 저장된다.
32bit pixel format 은 RGBA(24/8) color 를 나타낸다.
Image Storage
- 보통 RGB image format 은 R, G, B 각각에 8bit 를 사용한다. (이미지 하나에 원시정보 3MB 필요)
- image file format 에 압축이 추가됨. (Lossless vs. Lossy(손실압축))
- JPEG : lossy, threshold(임계값)에 따라 블록 compress.
- TIFF : lossless, 8/16bit RGB compress. binary image 에 널리 사용.
- PPM : lossless, 8bit RGB uncompressed
- PNG : lossless, 널리 사용되는 format.