[객체지향개발론] UML
2023. 8. 2. 22:10
📌 Model
- 우리가 실제로 만들 수 있을지, 미리 만들어 판단해 보는것.
- 실체가 아닌, (reality)실체의 (simplification)단순화이다.
- 해당 abstraction level 의 essential aspects 를 캡쳐(capture)한것.
- model 은 하나하나 각자의 aspect 를 띄고 있다 (eg. 평면도, 정면도, 측면도)
→ 모두 합쳐져서 하나의 시스템이 된다.
Visual Modeling
- standard graphical notation 을 사용한 모델링.
- Business Process <-[mapping]-> Computer System
모델을 만드는 이유
- 우리가 개발하고 있는 시스템을 더 잘 이해할 수 있게 하기 위해.
- complex system 전체를 이해할 수 없기 때문에, 시스템의 모델을 구축한다.
- 모델링을 통해 우리가 성취할 수 있는 목표 네 가지
- To visualize a system
- To specify the structure / behavior
- To give a blueprint
- To document the decisions
모델링의 principle, 원칙
- 모든 모델은 precision level 이 모두 다르게 표현되어야 한다.
- 하나의 모델만으로는 충분하지 않다. 종합적인 모델 세트로 이해해야 한다.
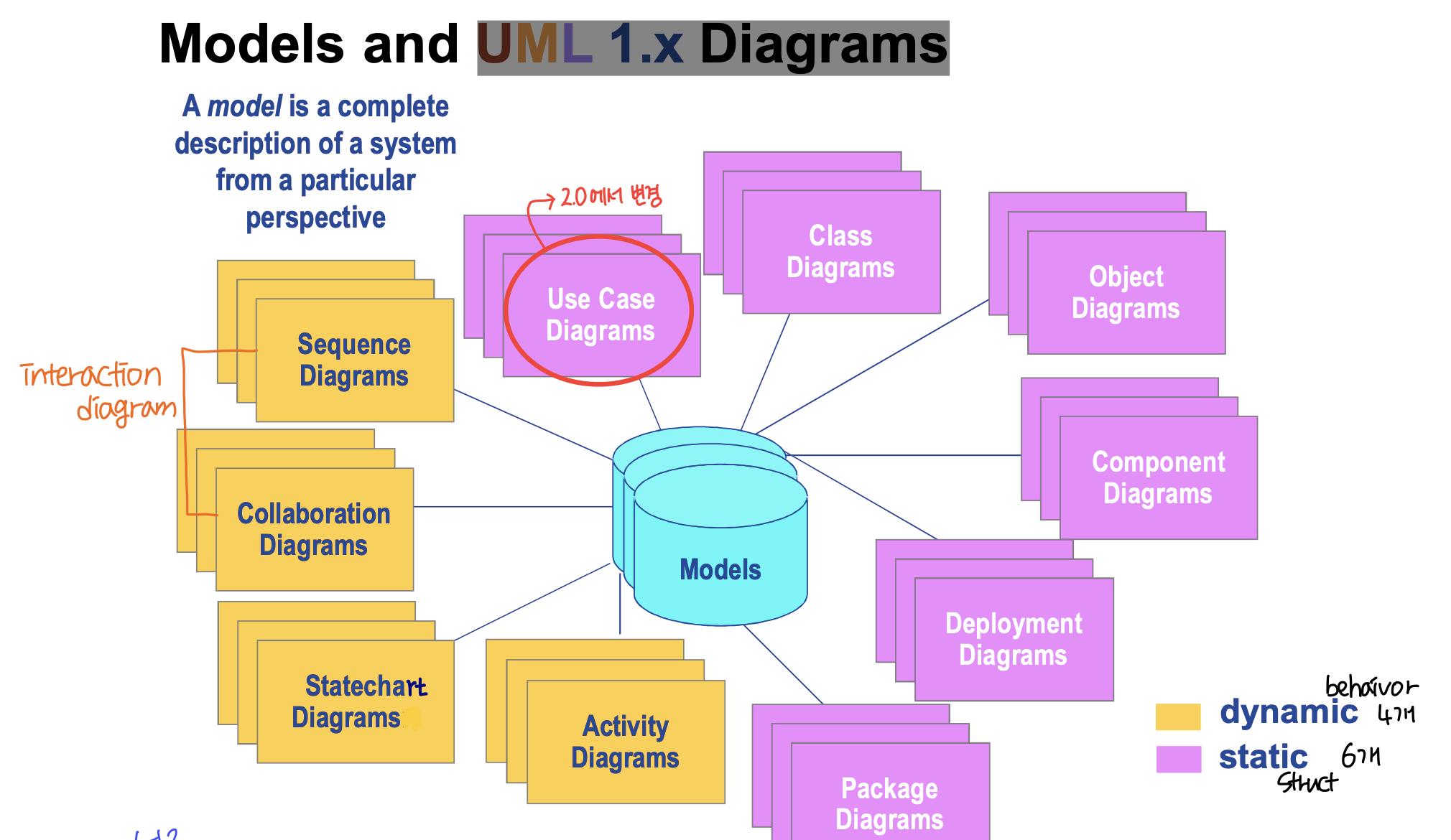
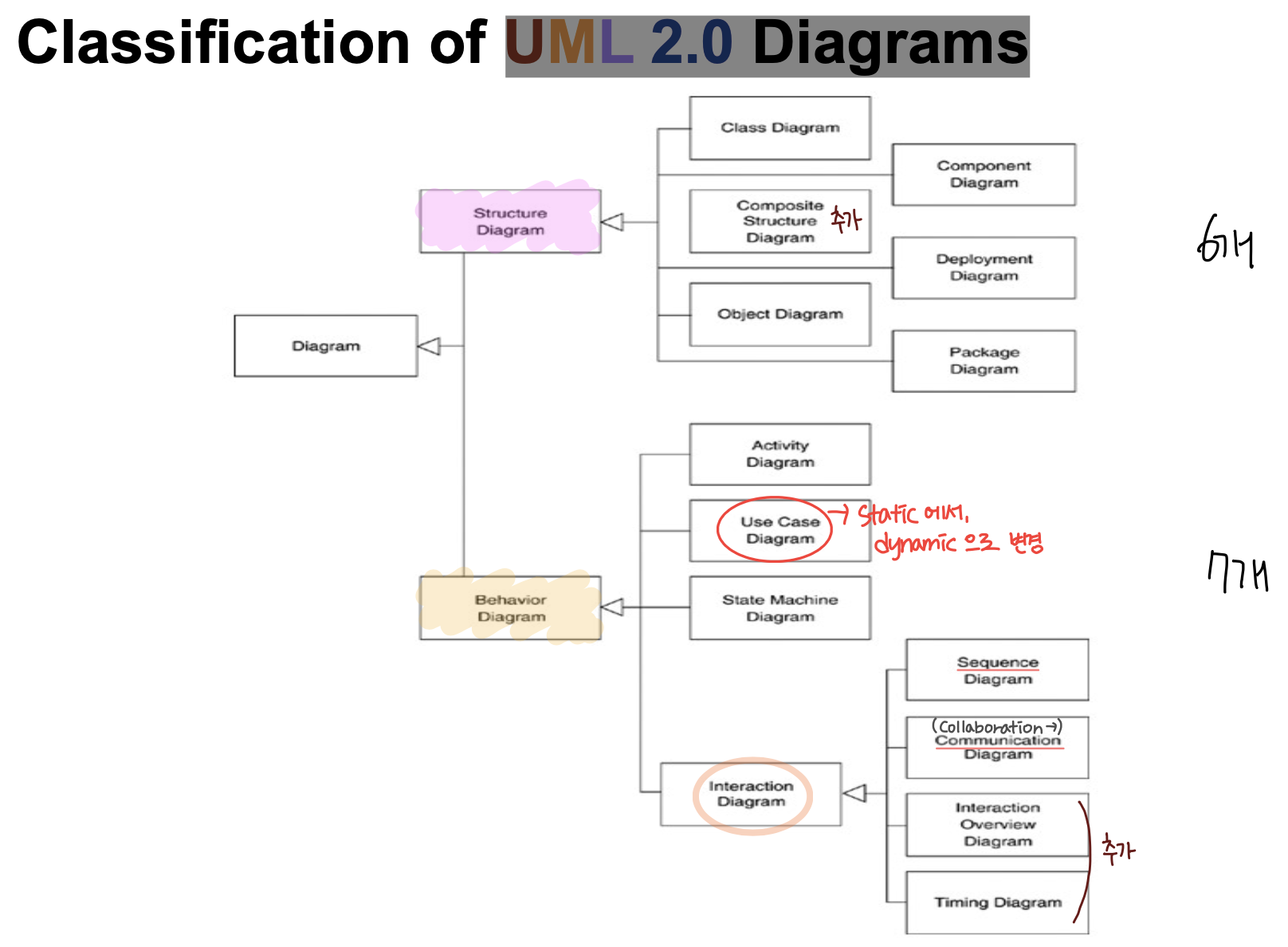
Static models(structural) vs. Dynamic models(behavior)
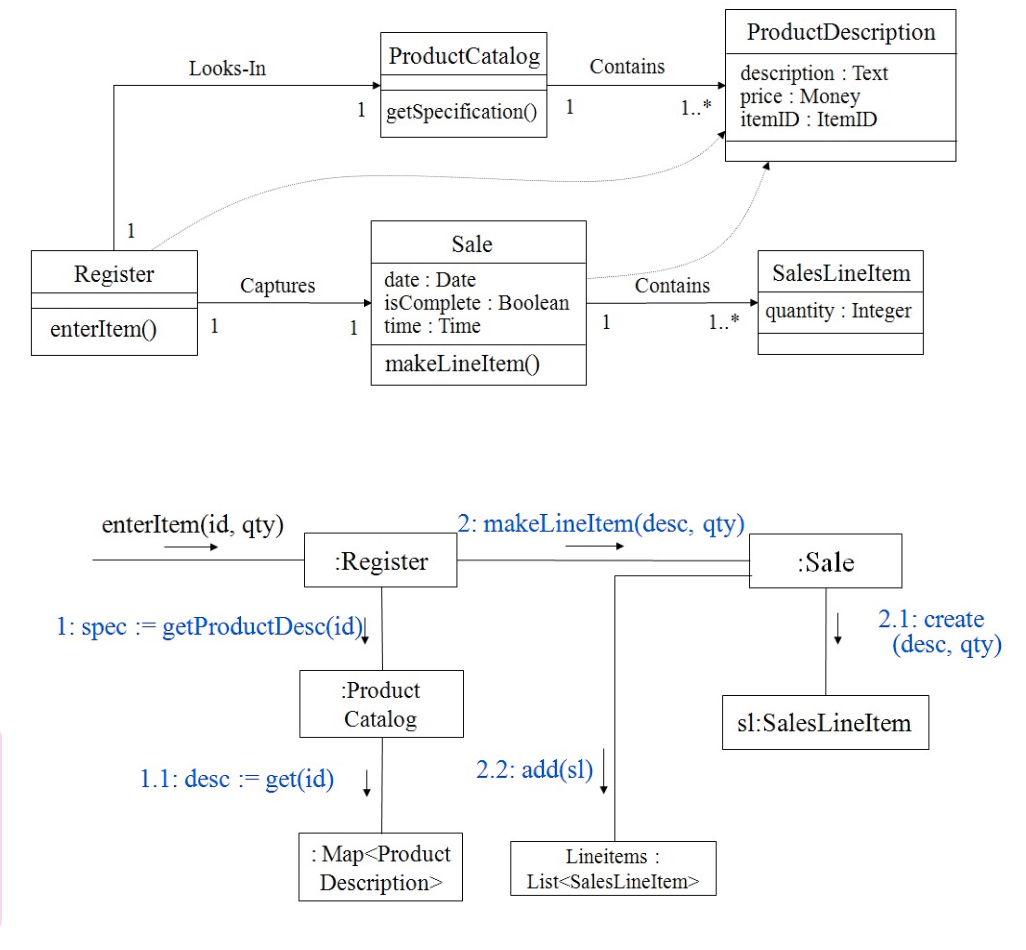
- Dynamic model 이 static model 을 끌고 가야하기 때문에, 상대적으로 Dynamic model 이 더 중요하다.
📌 UML
OO modeling 을 위한 standard visual modeling language.
- sketch, blueprint, programming language
Booch, OMT → Unified Modeling Language (UML)
- Visual Notation and semantics
- Process independent
📌 UP (Unified Process)
OOA & OOD & OOP

- A development process defines who is doing what, when and how to reach a certain goal, 개발 프로세스는 누가 특정 목표에 도달하기 위해 무엇을, 언제, 어떻게 하는지를 정의한다.
- In software engineering the goal is to build a software product or to enhance an existing one, 소프트웨어 공학에서 목표는 소프트웨어 제품을 만들거나 기존 제품을 향상시키는 것이다.
Object-Oriented Analysis
- requirement, problem domain 의 investigation, understanding, discovery 를 강조한다.
- logical solution 을 어떻게(how) 구성할지 걱정하지 않아도 된다.
- 모든 vocabularies 는 problem domain(실제세계)의 것을 쓴다.
Requirements Analysis
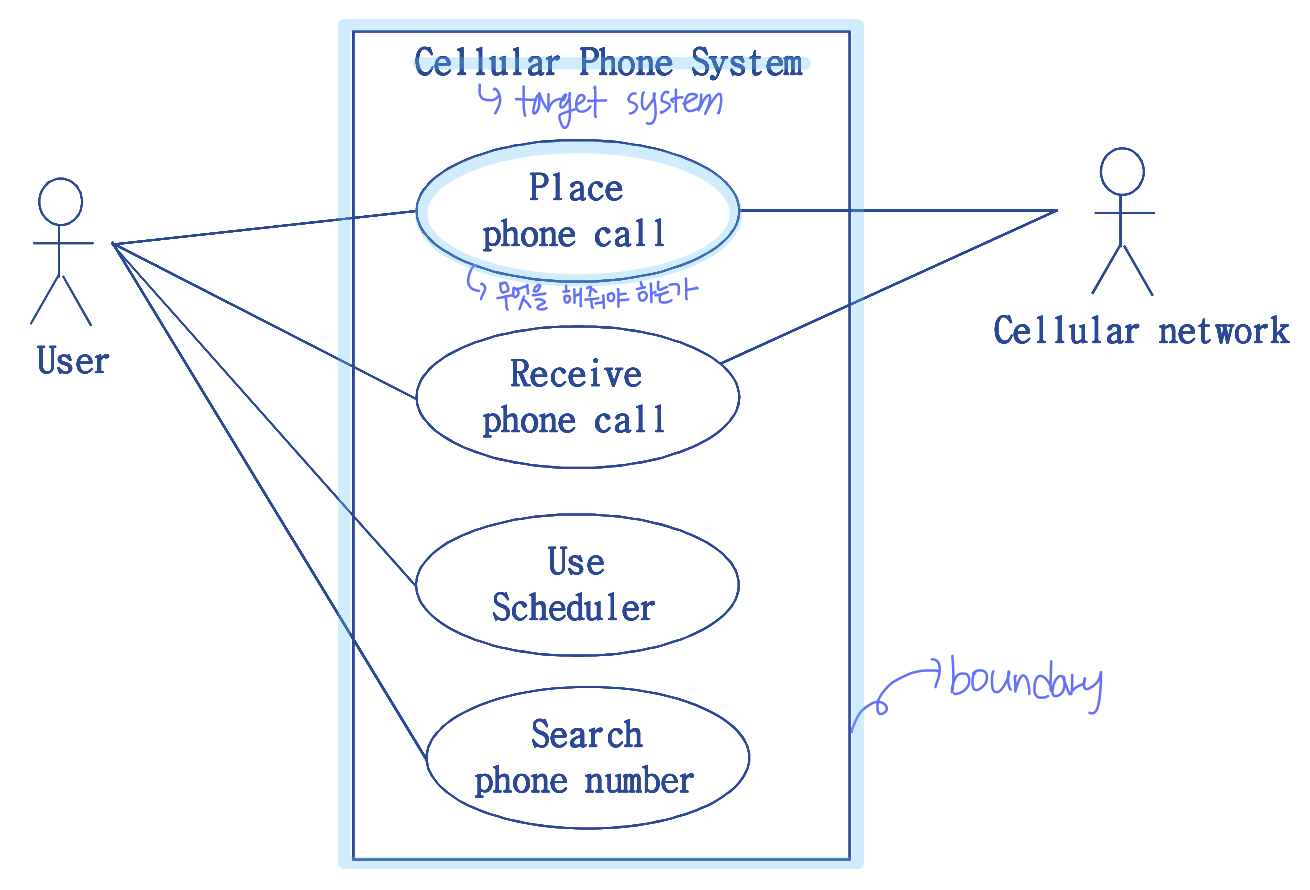
- functional & non-functional requirements 를 조사.
- Use-Case Model 을 사용해 functional requirements 를 캡쳐한다.
Object Analysis
- 시스템이 반영해야 하는 problem domain(실제 세계)의 domain object(실제 세계의 오브젝트) 를 조사.
- Domain-Model 사용.
Object-Oriented Designs
- 주로 개념 솔루션(conceptual solution)의 발명(invention) 및 적용(adaptation) 과정입니다.
- 사용하는 언어에 Independent 하다.
Object-Oriented Programmings
- implementation
Core of the UP
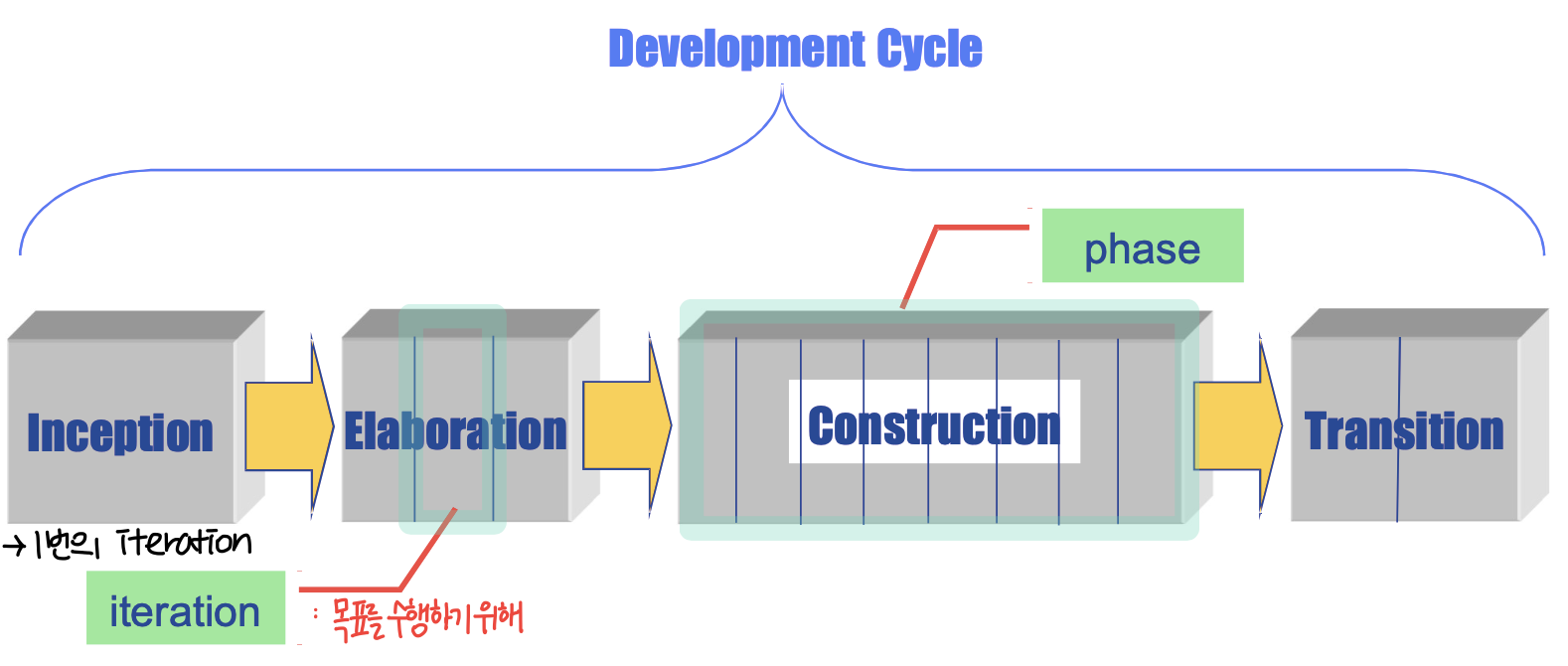
- Iterative and incremental development process
- Architecture-Central
- 여러번의 iterator 중 어느 것이라도 분석, 설계, 구현을 모두 진행한다.
- early iterator : 시스템의 전체적 structure(뼈대)를 경정하는데 집중한다.
- Use-Case Driven
Additional UP Best Practices
- high-risk & high-value issues 를 초기에 Tackle(해결)
- evaluation, feedback, requirement 를 위해 지속적으로 User 를 참여시킴.
- early iteration 에서 core architecture 구축.
- apply use case. test early, ofter.
- UML 로 시각적 모델링
- 요구사항을 신중히 관리
- Practice change request and configuration management
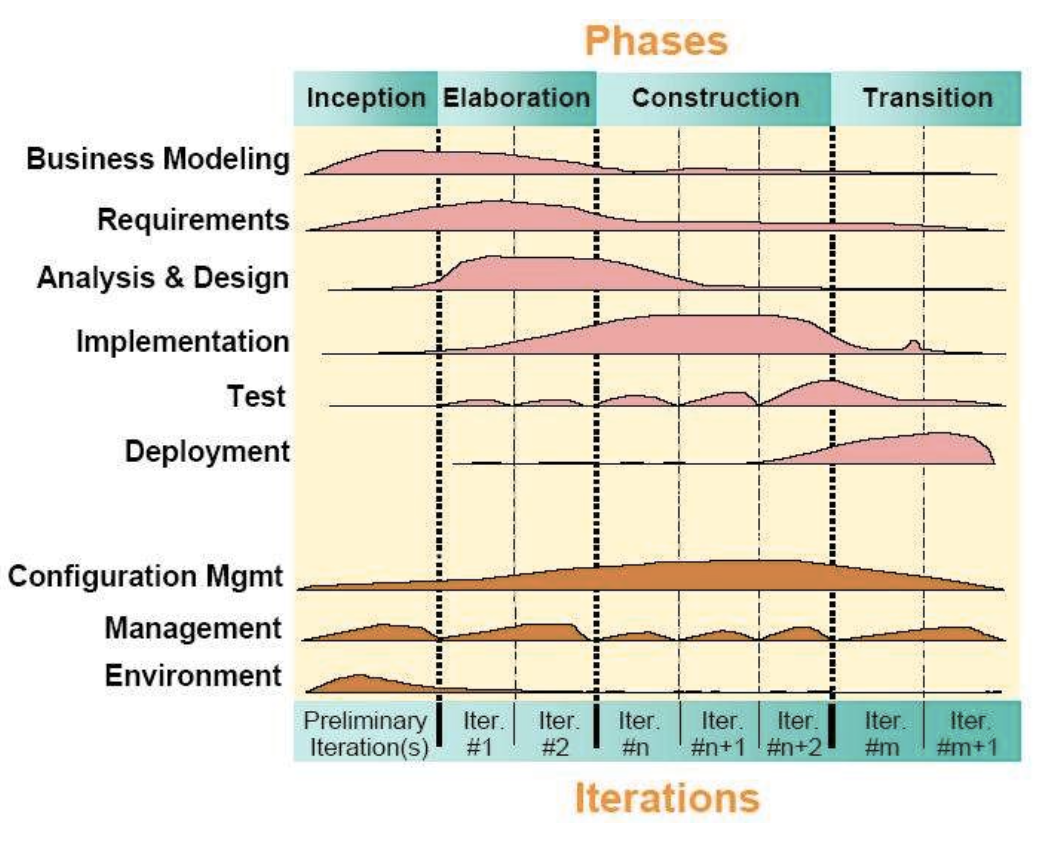
UP Develpment Cycle
Inception
- go / not to go 를 결정.
- Feasibility phase (가능성을 따져보는)
- vision, scope 예측 & vague estimates
Elaboration
- 틀을 제공.
- function requirements
- refined vision
- Implement core architecture
- resolve high risk
Construction
- 살을 붙임.
Transition
- release 준비
UP Disciplines and Artifacts
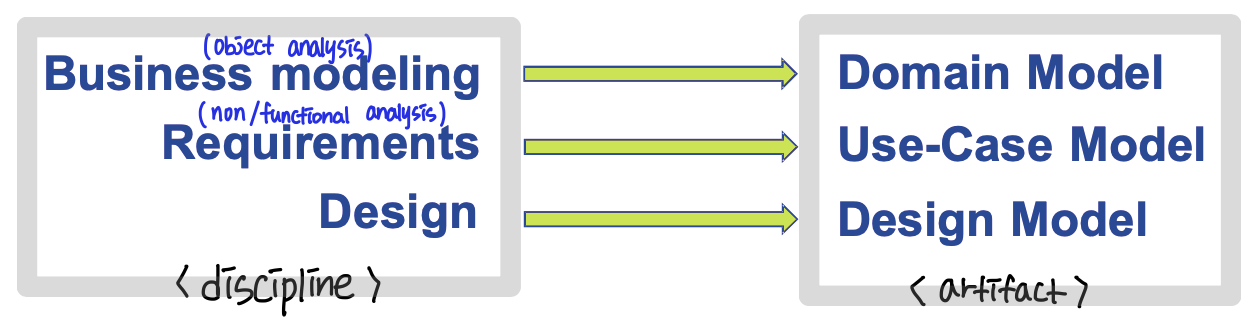
- discipline : 분석, 설계, 구현, 테스트
- artifact : 산출물
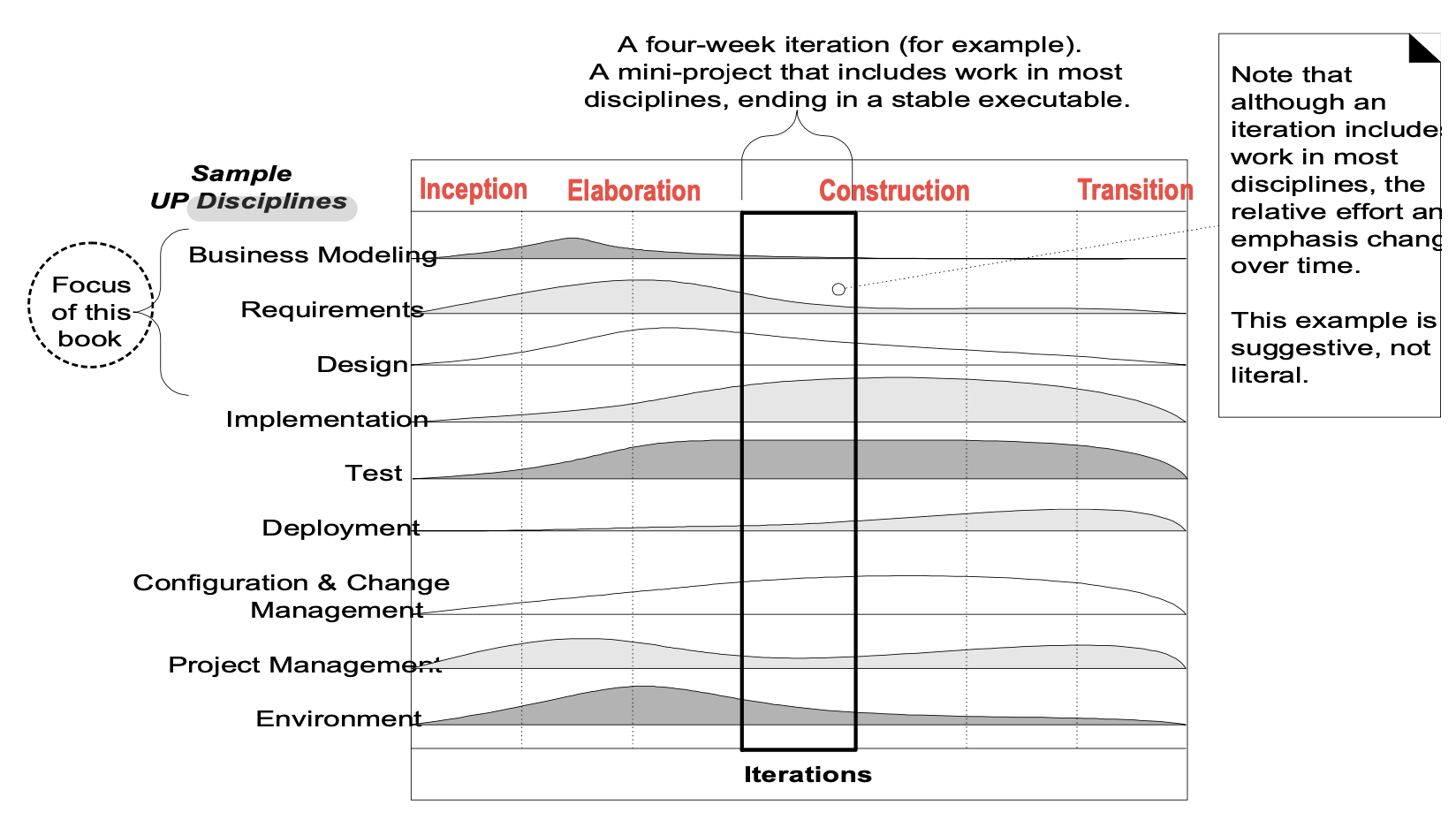
Development case
프로젝트 별로 커스텀한 개발 프로세스.
- UP ; meta process
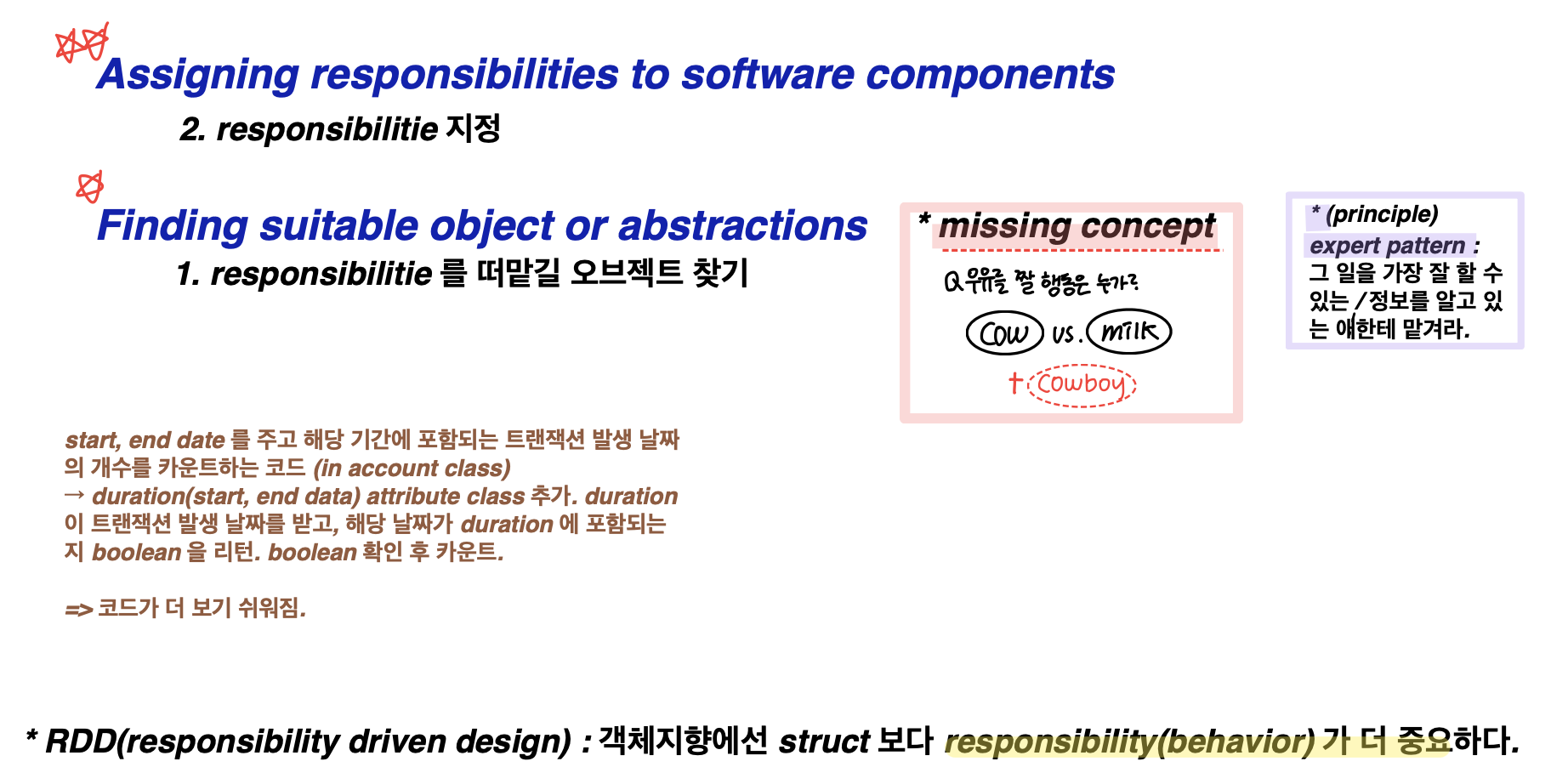
OOA & OOD 에서 가장 중요한 것
'* CS > 객체지향개발론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [객체지향개발론] 05 SSD and Domain Model(1) (0) | 2023.08.05 |
|---|---|
| [객체지향개발론] 04 Use Case (0) | 2023.08.04 |
| [객체지향개발론] Fundamental Concepts of OO (0) | 2023.07.30 |
| [객체지향개발론] Motivation for OO Modeling (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| [객체지향개발론] 00 Overview (0) | 2023.07.28 |